Figure 1: Donor HIV and ART status do not alter HIV-inhibitory function of semen extracellular vesicles.
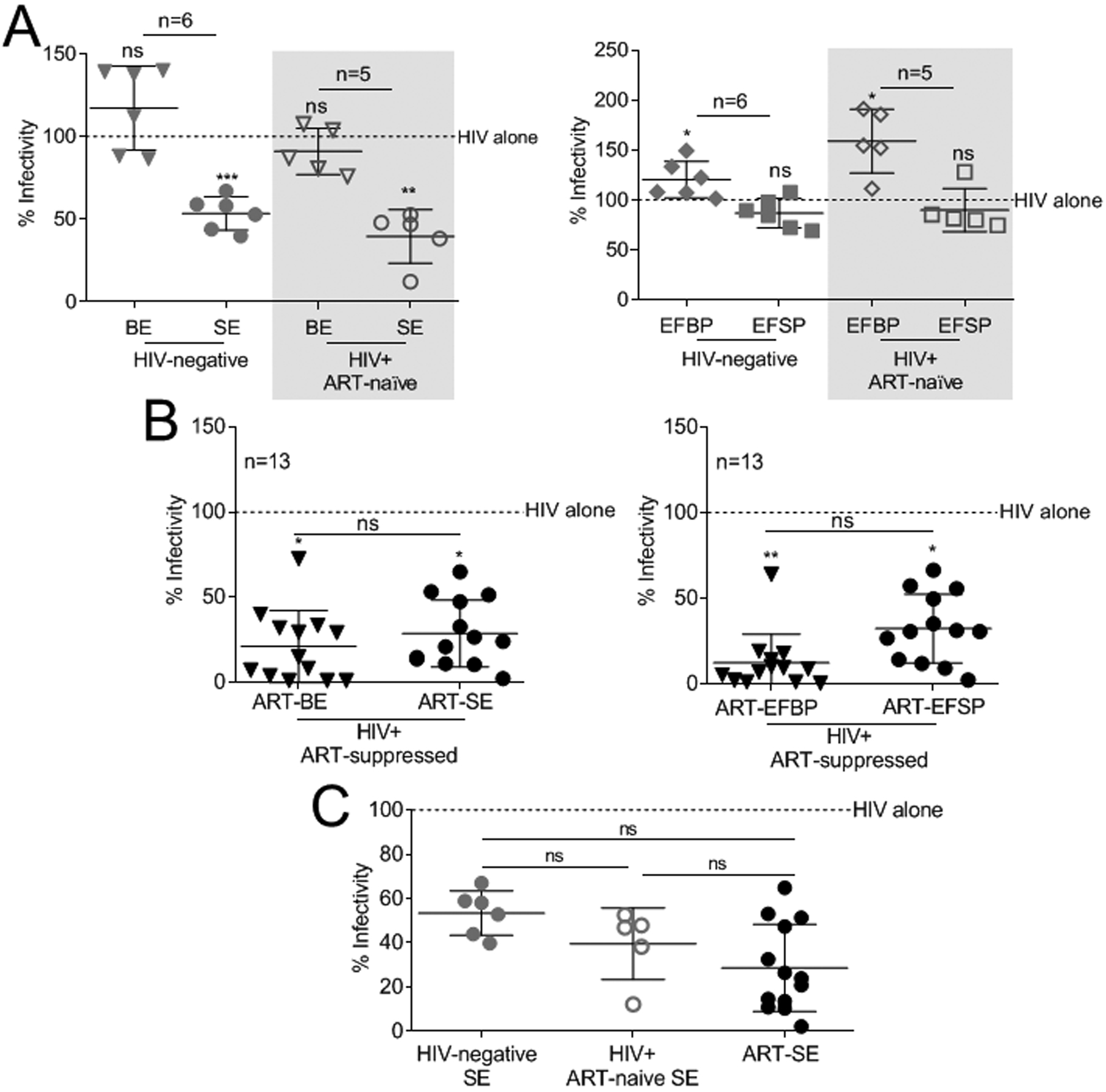
(A-C) Vehicle PBS or 100 μg/ml BE, SE, EFBP, and EFSP isolated from HIV-negative (n=6), HIV-positive ART-naïve (n=5), and HIV-positive ART-suppressed (n=13) donors were added simultaneously with 100,000RLU of HIV-1 NL4.3 virus to TZM-bl indicator cells for 24 h. TZM-bl infectivity was measured by luciferase reporter activity. Vehicle treated cells are set as reference at 100% (broken line). (A) Infectivity of HIV-1 treated with BE, SE, EFBP, and EFSP from HIV-negative and HIV-positive ART-naïve (shaded) donors. (B) Infectivity of HIV-1 treated with BE, SE, EFBP, and EFSP from HIV-positive ART-suppressed donors. Statistics was determined by comparing infectivity values from all donors to vehicle control for each treatment (A-B), and by comparing infectivity values between treatments (B). (C) Infectivity of HIV-1 treated with SE from HIV-negative, HIV-positive ART-naïve, and HIV-positive ART-suppressed donors. Statistics was determined by comparing infectivity values between donor cohorts (C). Significance was determined by student’s t test. *=P<0.05, **=P<0.01, ***=P<0.001. Error bars are SD of biological replicates from the mean of triplicate measurements. ns= not significant.
