Figure 3.
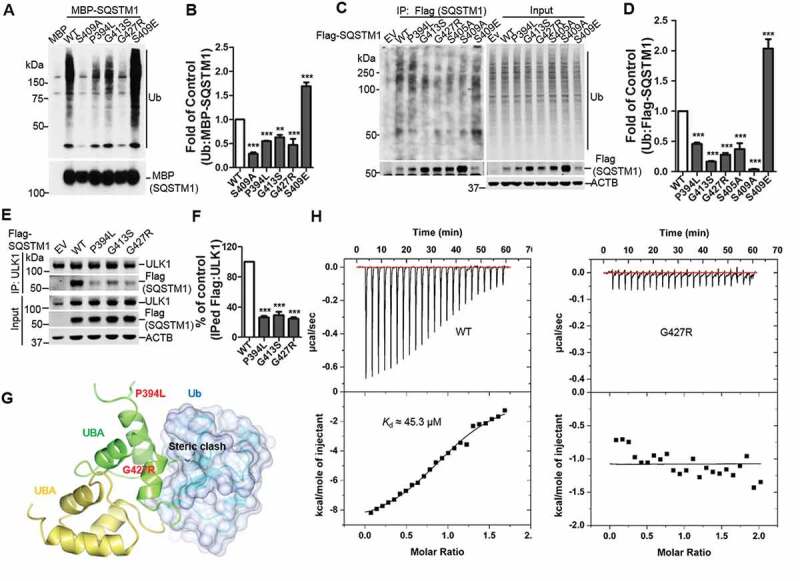
ALS-FTLD-linked mutations of SQSTM1 in the UBA domain affect its binding to ubiquitin and ULK1. (A) MBP and MBP-SQSTM1 variants were subjected to pull down in the presence of K63-linked ubiquitin peptides. Interaction of SQSTM1 variants and Ubs was detected by immunoblot analysis with Ub antibody. (B) Ubiquitin levels pulled down by the MBP-SQSTM1 variants were normalized to protein input and compared to that of MBP-SQSTM1 WT protein. One-way ANOVA test was used and followed by Tukey’s post hoc test, and values are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 6). ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001. (C) Cellular lysates of sqstm1 KO MEFs transfected with Flag-SQSTM1 variants were incubated with sqstm1 KO MEFs lysates treated with MG132, followed by IP with anti-Flag antibody. (D) Quantification of the results from C was obtained by normalizing the levels of immunoprecipitated Ub to each Flag-SQSTM1 variant, and then variants were normalized to WT. One-way ANOVA test was used and followed by Tukey’s post hoc test, and values are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4). *** p < 0.001. (E) Cellular lysates of sqstm1 KO MEFs transfected with Flag-SQSTM1 variants were immunoprecipitated with anti-ULK1 antibody. Immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibodies was followed. (F) Quantification of the results from E was obtained by normalizing levels of immunoprecipitated Flag to the level of input, then further normalized to the level of immunoprecipitated ULK1. One-way ANOVA test was used and followed by Tukey’s post hoc test, and values are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 3). *** p < 0.001. (G) The SQSTM1P394L and SQSTM1G427R mutations are mapped onto the model structure of the SQSTM1 UBA domain complexed with ubiquitin. The mutated residues are shown as stick models. (H) Binding affinities of SQSTM1 UBA WT or UBAG427R mutant to mono-Ub were measured by ITC. Representative ITC profiles are shown.
