Figure 7.
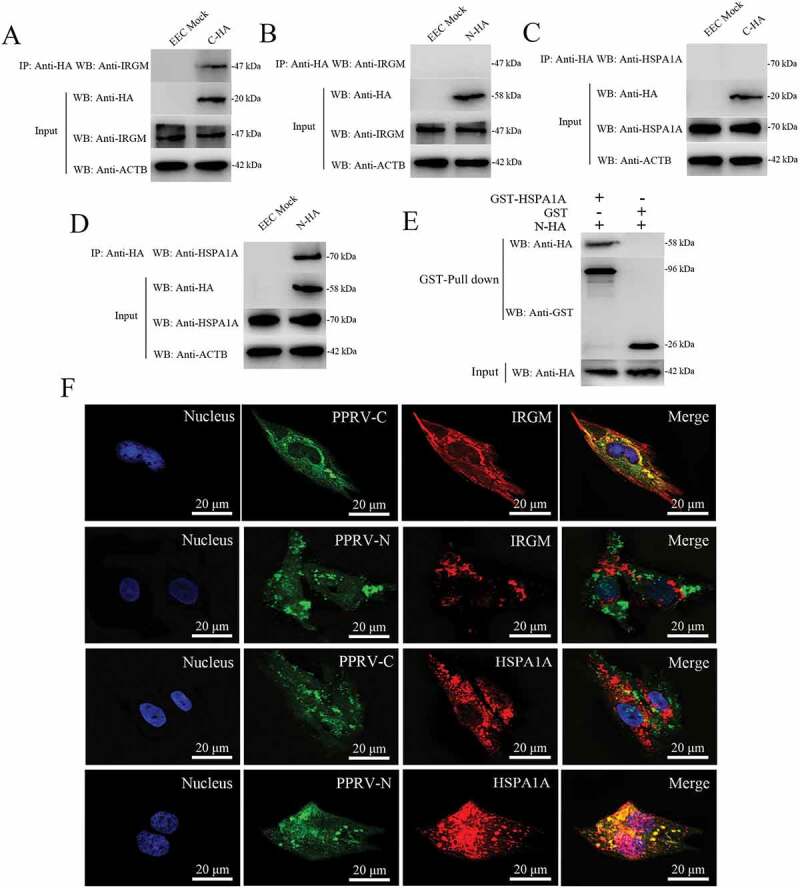
Physical interaction and co-localization of IRGM and HSPA1A with viral proteins. (A and B) Co-IP assay results demonstrating that endogenous IRGM binds C-HA but not N-HA in transfected cells. EECs were transfected with pCDNA3.1-C-HA or pCDNA3.1-N-HA for 48 h and harvested. Cell lysates from the transfected cells and from untransfected control cells were immunoprecipitated with an antibody against HA and then subjected to immunoblotting. (C and D) Co-IP assay results demonstrating that endogenous HSPA1A binds N-HA but not C-HA in transfected cells. EECs were transfected with pCDNA3.1-C-HA or pCDNA3.1-N-HA for 48 h and harvested. Cell lysates from the transfected cells and from untransfected control cells were immunoprecipitated with an antibody against HA and then subjected to immunoblotting. (E) GST pulldown assay results demonstrating the physical and direct interaction between HSPA1A and PPRV-N. Glutathione beads conjugated to GST or a GST-HSPA1A fusion protein were incubated with recombinant N-HA protein. After washing, the proteins were eluted from the beads, and SDS-PAGE was performed. Expression of the N protein was detected by immunoblotting with an anti-HA antibody. GST and GST-HSPA1A protein expression was confirmed by immunoblotting with an anti-GST antibody. (F) IRGM co-localizes with PPRV-C, and HSPA1A co-localizes with PPRV-N. EECs were transfected with pCDNA3.1-C-HA or pCDNA3.1-N-HA for 48 h. The transfected cells were fixed and processed for indirect immunofluorescence analysis using antibodies against HA (green), IRGM (red) and HSPA1A (red). The cell nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342 solution. Scale bars, 20 μm.
