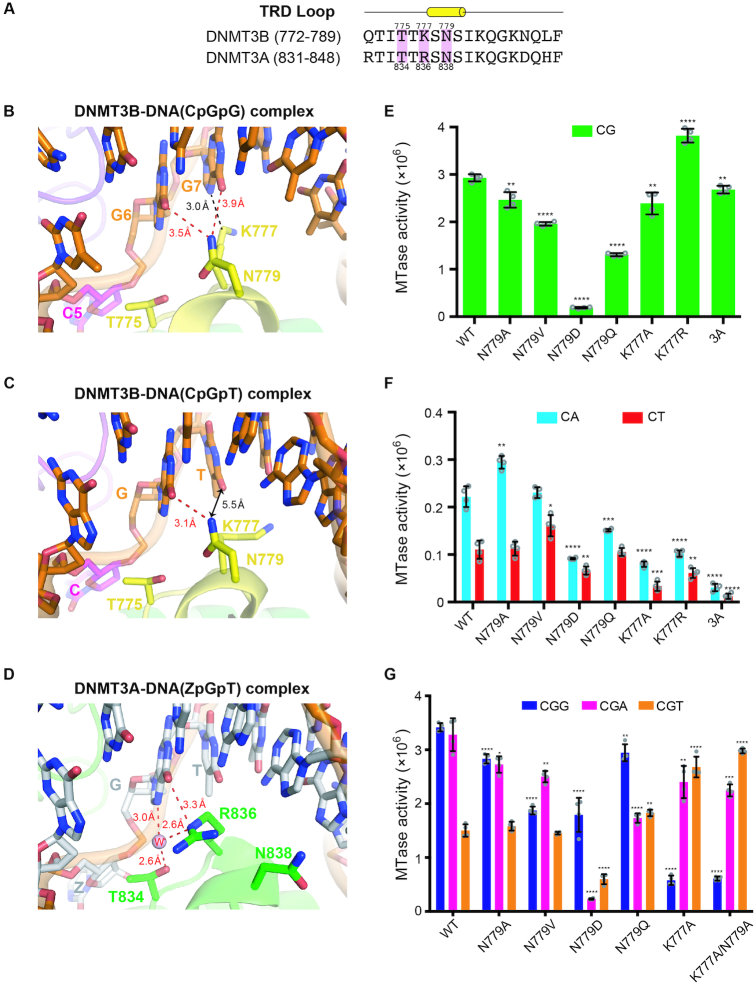
Figure 4.
Specific recognition of the guanines in CpGpG sites by DNMT3B. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the TRD loop of human DNMT3B and DNMT3A. Key conserved residues are shaded in pink. (B) In the crystal structure of DNMT3B–3L–DNA (CpGpG) complex, residue N779 (Nδ atom) in the TRD loop forms hydrogen bonds with the guanine (G6, O6 atom) of the target CpG site and the flanking guanine (G7, O6 atom) downstream of the CpG site. Residue K777 (Cϵ atom) interacts with the flanking guanine through van der Waals interactions. (C) In the crystal structure of the DNMT3B–3L–DNA (CpGpT) complex, residue N779 (Nδ atom) in the TRD loop forms a hydrogen bond with the guanine (G6, O6 atom) of the target CpG site. Residue K777 does not interact with the flanking thymine beyond a distance of 5.5 Å. (D) Residue R836 of DNMT3A interacts with the guanine of the target ZpG site via a hydrogen bond and water-mediated hydrogen bonds. Methylation activities of DNMT3B, its mutants and DNMT3A for 24-bp DNA containing CpG (E), CpA or CpT (F), as measured by methyltransferase-Glo assays (in luminescence, RLU, n = 4). (G) Methylation activities of DNMT3B and its mutants for 24-bp DNA containing CpGpG, CpGpA or CpGpT, as measured by methyltransferase-Glo assays (in luminescence, RLU, n = 4). For (E)–(G), error bars denote SD; *P < 0.1, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 and ****P < 0.0001. Statistical significance (P-values) was determined by two-tailed Student's t-test.