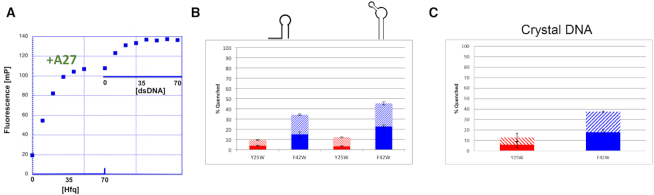
Figure 3.
Hfq uses the same interface to bind dsDNA and dsRNA but a different interface to bind distal-face binding polyA. (A) Fluorescence polarization demonstrates that A27 RNA and dsDNA can simultaneously bind to Hfq on distal and proximal faces, respectively. Hfq was first titrated into fluorescent A27 RNA until saturation was reached. DNA was then titrated into the same mixture and a second binding event was observed. (B) Tryptophan Fluorescence quenching reveals that hairpin RNAs (Left) site A, sequence AUUUUUUCGAAUCGAAAGGUUCA, (Right) Hairpin 2, sequence (CAUGAUUCUUAUACGUACGACGGAAGAUGAGAAUUAUGGU) preferentially bind to and quench the proximal face (F42W) over the distal face (Y25W). The solid portion of each column is quenching by the addition of 1 μM protein and the hatched portion of each column is quenching by the addition of 4 μM protein. (C) Tryptophan fluorescence quenching reveals that the dsDNA oligodeoxynucleotide, which was used in crystallization, preferentially binds to and quenches proximal face residue F42W and not distal face residue Y25W.