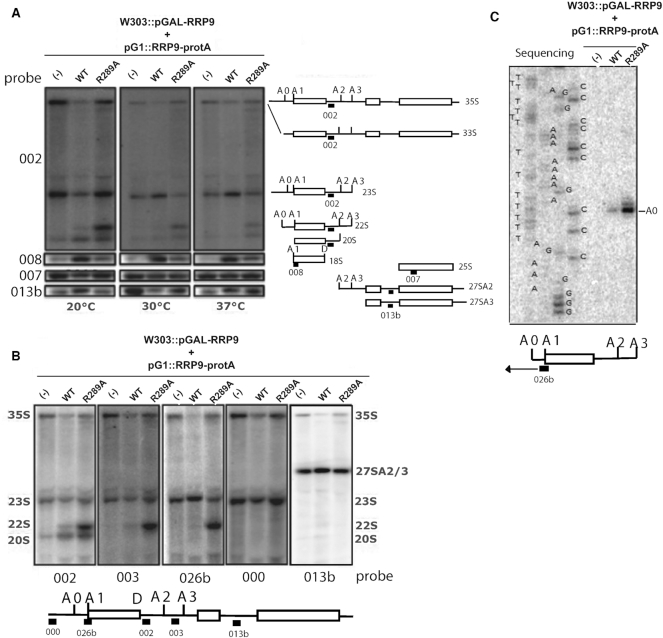
Figure 3.
The Rrp9-R289A mutation affects pre-rRNA early cleavages at sites A1 and A2 leading to strong accumulation of the aberrant 22S RNA at 20°C. (A) The different RNA species produced from the 35S pre-rRNA at 20, 30 and 37°C were detected by northern-blotting using specific probes, indicated on the left side of panel A (Supplementary Table S1) (002 downstream of the 18S sequence, 008 close to the 5′ extremity of the 18S, 007 in the 5′-terminal part of the 25S, and 013b between the 5.8S and 25S sequence, in the ITS2 segment, as drawn right of panel A). Cells were transformed with an empty pG1 plasmid or pG1 plasmids expressing WT- or R289A–Rrp9. The cleavage steps generating the 18S rRNA from the 35S pre-rRNA are schematized on the right side of the panel. Positions of the probes are indicated on the schematic representations of the various intermediates. Upon expression of Rrp9 R289A, an accumulation of 22S RNA is detected, especially at 20°C and 18S production is decreased at all the tested temperatures. (B) The identities of cleavage sites occurring at 20°C in the pre-rRNA were determined by northern-blotting using five discriminating probes shown under the panel (Supplementary Table S1). Briefly, the binding site of probe 002 was located between sites A2 and D enabling detection of the 35S pre-rRNA and the 23S, 22S and 20S RNA intermediates. The probe 003 binding sequence was located between sites A2 and A3. This probe was dedicated to the detection of intermediates that were not cleaved at site A2, namely, the 35S, 23S and 22S RNAs, but not the 20S intermediate. Probe 026b hybridized between sites A0 and A1 and revealed the intermediates that were not cleaved at site A1, thus detecting the 35S, 23S and 22S pre-rRNAs. Probe 000 was binding upstream of site A0, revealing only the 35S pre-rRNA and the 23S intermediate that is not cleaved at site A0. Finally, probe 013b was binding downstream from site A3, and was only detecting the 35S pre-rRNA and intermediates involved in the 5.8S and 25S maturation. The absence of binding of probes 000 and 013b and the binding of probes 002, 003 and 026b to the abnormally accumulated intermediate species confirmed that it was the 22S intermediate cleaved at sites A0 and A3 without cleavage at sites A1 and A2. (C) To define the 5′ extremity of the 22S RNA intermediate, a primer extension experiment was performed with oligonucleotide 026b binding upstream of site A1 as depicted in the cartoon at the bottom of the panel. Products of the primer extension were fractionated in parallel with the products of sequencing reactions generated with the same primer (026b). Site +1, the 5′ end of 35S and 23S RNAs, is too far from the primer to be detected.