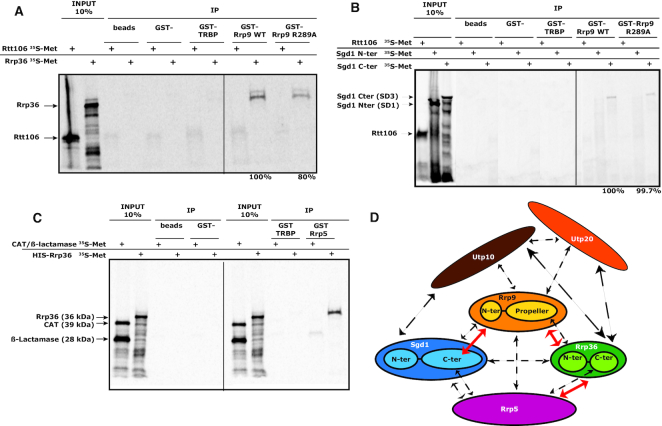
Figure 5.
Some of the detected Y2H interactions correspond to direct interactions. (A–C) GST-tagged wild-type Rrp9, GST-tagged R289A mutant Rrp9, a GST-tagged non-relevant protein (GST-TRBP) or GST alone were bound to glutathione sepharose beads and incubated in the presence of Rrp36, Sgd1 domains or control proteins (Rtt106, CAT and β-Lactamase) labeled with [35S]-methionine. Protein–protein interactions were revealed by autoradiography. As shown by GST pull-down assays, interactions of Rrp36 (A) and the C-terminal domain of Sgd1 (B) with Rrp9 are direct interactions. Rrp36 also interacts directly with Rrp5 (C). The strength of the Rrp9-Rrp36 interaction is decreased by the Rrp9 R289A mutation by 20% (A), which is confirmative of Y2H results. (D) Schematic representation of the interaction network characterized for proteins Rrp9 and Sgd1, Rrp36, Rrp5, Utp10 and Utp20. Dashed arrows represent the Y2H interactions detected between proteins and/or protein sub-fragments (Figure 4, Supplementary Table S2). Plain red arrows represent direct interactions. Due to solubility problems, only three direct interactions were tested. Therefore, direct interactions of Rrp9, Rrp36, Rrp5 and Sgd1 with Utp10 and Utp20 were not tested.