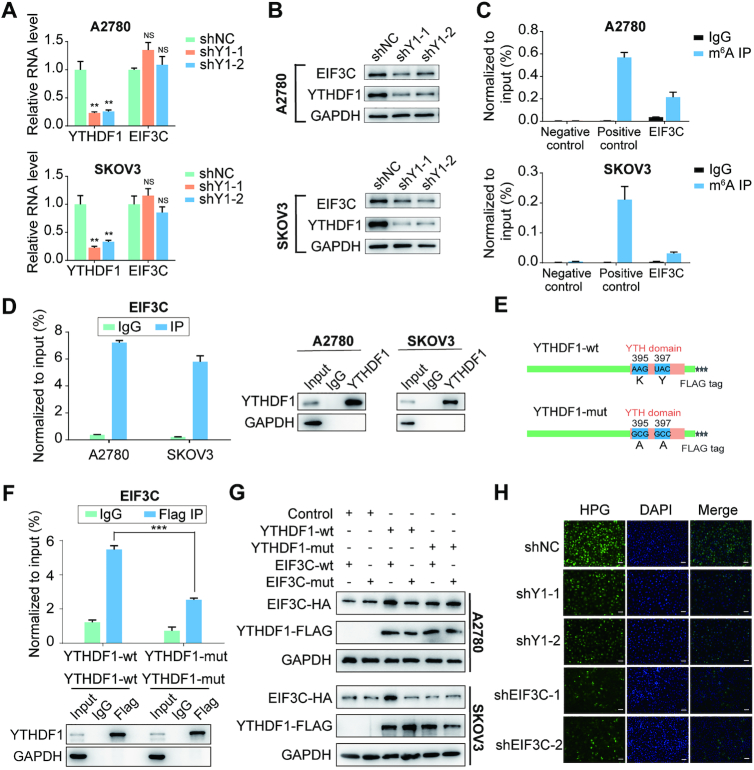
Figure 6.
YTHDF1 regulates EIF3C translation in an m6A-dependent manner. (A) Relative RNA level of EIF3C in A2780 and SKOV3 upon YTHDF1 knockdown. (B) Western blot detected the protein level of EIF3C in A2780 and SKOV3 cells upon YTHDF1 knockdown. (C) Gene-specific m6A qPCR validation of m6A levels in A2780 and SKOV3 cells. Primers to m6A negative region of EEF1A as the negative control and primers to m6A postive region of EEF1A as the positive control. (D) YTHDF1 RIP followed by RT-qPCR confirmed the interaction between YTHDF1 and EIF3C mRNA. (E) Schematic representation of wild-type (YTHDF1-wt) and mutant (YTHDF1-mut) YTHDF1 constructs. (F) RIP-derived RNA and protein in A2780 cells were measured by RT-qPCR and western blot, respectively. GAPDH was used as the negative control in western blot assays. (G) Western blot confirmed HA-tagged EIF3C expression in A2780 or SKOV3 cells co-transfected with empty vector, wild-type or mutant Flag-tagged YTHDF1 and wild-type or mutant HA-tagged EIF3C. (H) Nascent protein synthesis was detected by HPG incorporation upon YTHDF1 knockdown or EIF3C knockdown in A2780 cells. Scale bar, 100 μm. Data are shown as means ± S.D. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, NS, not significant.