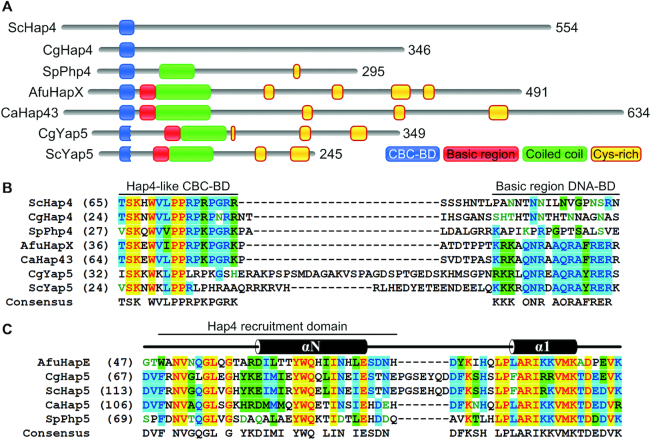
Figure 11.
Domain architecture of fungal transcription factors that require the CBC as DNA-binding scaffold for their function. (A) The Hap4 activators of respiratory gene expression in S. cerevisiae (Sc) and C. glabrata (Cg) contain the complete 16 aa Hap4-like CBC-BD, but lack a basic region DNA-BD (25,63). The same applies to Php4 in S. pombe (Sp), which represses iron-dependent pathways in response to iron deficiency (64). A. fumigatus (Afu) HapX and its ortholog Hap43 in C. albicans (Ca) are bZIP transcription factors that include the full 16 aa Hap4-like CBC-BD. Both HapX and Hap43 have dual functions in regulation of iron homeostasis, thereby acting as both repressor and activator depending on iron availability (3,10,20). Yap5 bZIPs contain a degenerated Hap4-like domain and activate the high iron stress response in C. glabrata and S. cerevisiae (21,25). Full and rudimentary Hap4-like domains required for CBC-binding are shown in blue. Basic regions, coiled coil domains and Cysteine-rich regions are depicted in red, green and yellow, respectively. (B) Amino acid sequence alignment of the Hap4-like CBC-BD and basic region DNA-BD spanning regions in the N-Termini of regulatory CBC subunits shown in (A). (C) Amino acid sequence alignment of the Hap4 recruitment domain of fungal Hap5 orthologs. Secondary structures (α: helix) are indicated for the HapE subunit from A. nidulans (30). Identical residues are marked in yellow, residues conserved in 50% of the sequences are shaded in light blue and blocks of similar residues are marked in green. Alignments were performed with AlignX (Vector NTI Advance 11).