Figure 8.
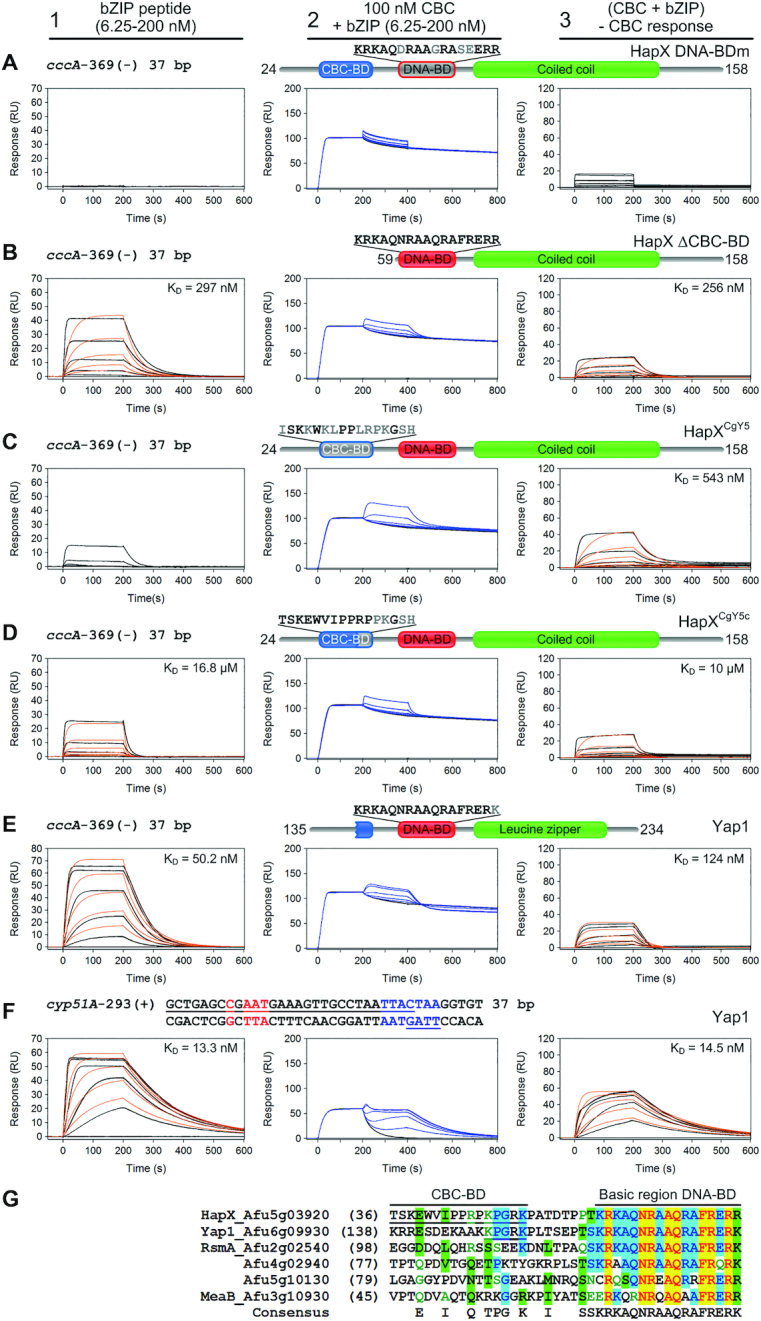
Loss of cooperative CBC:HapX binding is elicited by HapX DNA-BD mutations, deletion or modifications of the CBC-BD. SPR sensorgrams of HapX (A, B), HapX/CgYap5 hybrids (C, D) or Yap1 (E, F) binding to DNA (panel 1), and bZIP peptides to preformed CBC:DNA complexes (panel 2) are shown. Aa residues that differ from the native HapX sequence are marked in gray. Nt underlined in black are covered by the CBC and nt marked in blue represent the A. fumigatus HapX DNA-binding site in the cyp51A promoter. The overlapping Yap1-like half-sites in the cyp51A promoter are underlined in blue. Binding responses of the indicated bZIP concentrations injected in duplicate (black lines) are shown overlaid with the best fit derived from a 1:1 interaction model including a mass transport term (red lines). Binding responses of CBC:DNA:bZIP ternary complex formation (panel 2, blue lines) were obtained by concentration dependent co-injection of bZIPs on preformed binary CBC:DNA complexes. Sensorgrams in panel 3 depict the association/dissociation responses of bZIPs on preformed CBC:DNA and were generated by CBC response subtraction (co-injection of buffer) from bZIP co-injection responses. (G) Amino acid sequence comparison of the HapX CBC-BD and DNA-BD spanning region with A. fumigatus bZIPs carrying the basic region signature sequence of the fungal Yap1/Pap1 subfamily. Sequences are aligned according to similarity of the basic regions. The HapX CBC-BD and a rudimentary CBC-BD in the N-terminal region of Yap1 are underlined.
