Fig 2. Effects of NTD phosphorylation mutants on capsid assembly and RNA packaging.
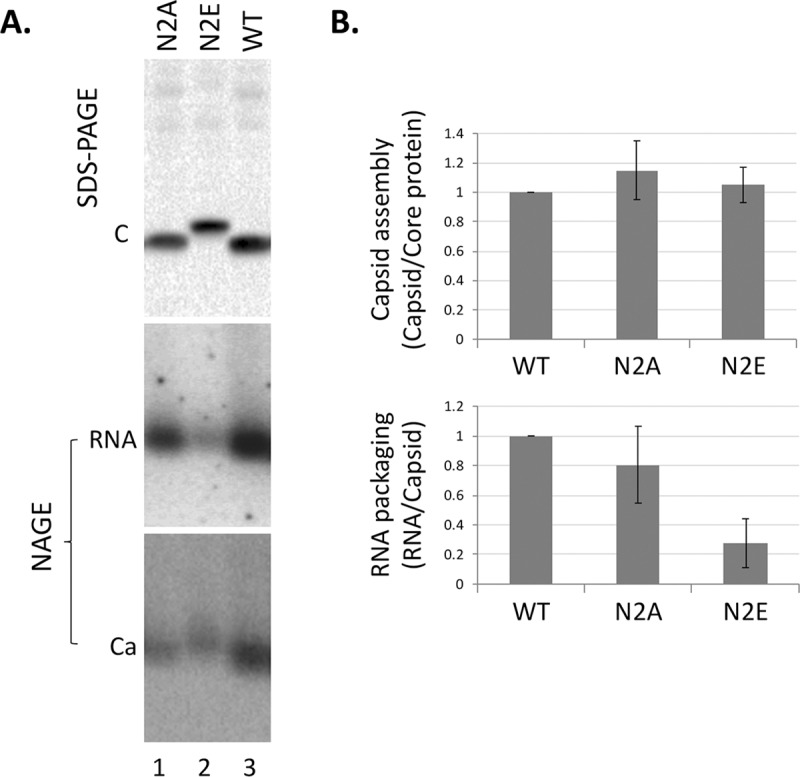
The HBV replicon construct expressing the N2A or N2E mutant, or WT HBc was transfected into HepG2 cells. Transfected cells were lysed five days later. A. Levels of HBc proteins (top) were measured by western blot analysis using the T2221 anti-HBC NTD mAb following resolution by SDS-PAGE (top). Assembled capsids (bottom) and packaged RNA (middle) were detected by using a plus strand specific RNA probe and the Dako anti-HBc polyclonal antibody, respectively, following resolution by native agarose gel electrophoresis (NAGE) and transfer to nitrocellulose membrane. C, HBc protein; Ca, HBV capsid. RNA signals were detected by phosphorimaging scan and protein signals by chemiluminescence scan. B. Quantitative results from multiple experiments shown in A. Capsid assembly efficiency (top) was determined by normalizing the levels of capsids measured following NAGE to those of HBc proteins following SDS-PAGE, with the efficiency from WT HBc set to 1.0. RNA packaging efficiency (bottom) was determined by normalizing the levels of RNA packaging to those of capsids, with the efficiency from WT HBc set to 1.0.
