Figure 1.
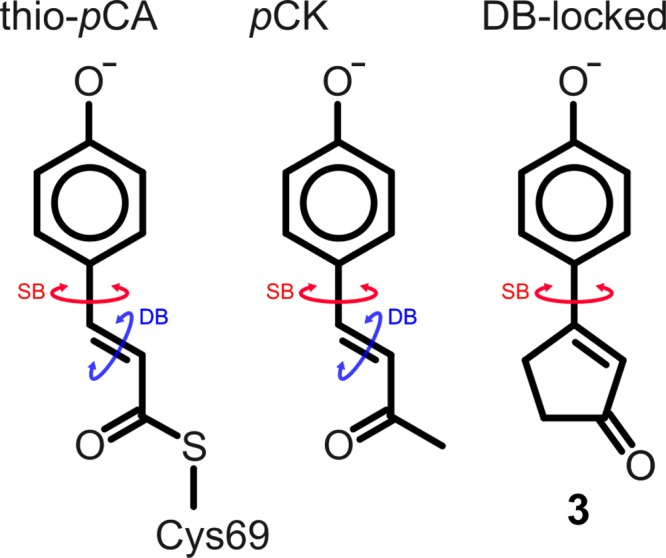
In PYP, the para-coumaric acid (pCA) chromophore is deprotonated and covalently attached to the protein via a thioester bond with a cysteine side chain (thio-pCA, left structure). The pCK analogue (middle) has a methyl group instead of a thioester but exhibits very similar optical properties compared with thio-pCA.5 In this work, the double-bond (DB)-locked analogue (3, right) was studied. The cyclic structure prevents isomerization around the double bond, and only single-bond (SB) isomerization is possible.
