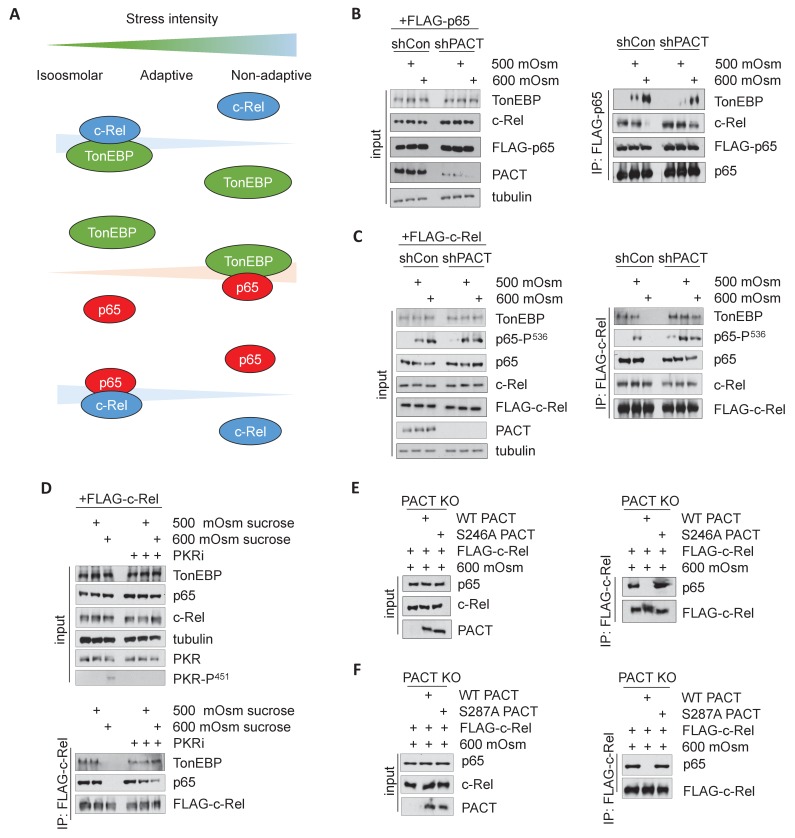
Figure 6. Activation of the PACT/PKR signaling axis inhibits the interaction of NF-κB c-Rel with NF-κB p65 or TonEBP, and increases the interaction of NF-κB p65 with TonEBP.
(A) As stress intensity increases, NF-κB c-Rel/TonEBP and NF-κB c-Rel/NF-κB p65 species dissociate, while NF-κB p65/TonEBP species accumulate. (B) Control and shPACT MEFs were transfected with a FLAG-NF-κB c-Rel construct, then treated with 500 or 600 mOsm sucrose for 3 hr. Total cell extracts and FLAG-co-immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed via western blot. (C) Control and shPACT MEFs were transfected with a FLAG-NF-κB p65 construct, then treated with 500 or 600 mOsm sucrose for 3 hr. Total cell extracts and FLAG-co-immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed via western blot. (D) WT MEFs were transfected with a FLAG-NF-κB c-Rel construct, then treated with the indicated stress for 3 hr in the presence or absence of a small molecule inhibitor of PKR. Total cell extracts and FLAG-co-immunoprecipitated proteins were analyzed via western blot. (E) PACT KO MEFs were reconstituted with WT- or S246A-PACT, and transfected with a FLAG-NF-κB c-Rel construct. After treatment with 600 mOsm sucrose for 3 hr, complexes were co-immunoprecipitated with the FLAG antibody and analyzed via western blot, in parallel with total cell extracts. (F) PACT KO MEFs were reconstituted with WT- or S287A-PACT, and transfected with a FLAG-NF-κB c-Rel construct. After treatment with 600 mOsm sucrose for 3 hr, complexes were co-immunoprecipitated with the FLAG antibody and analyzed via western blot in parallel with total extracts.