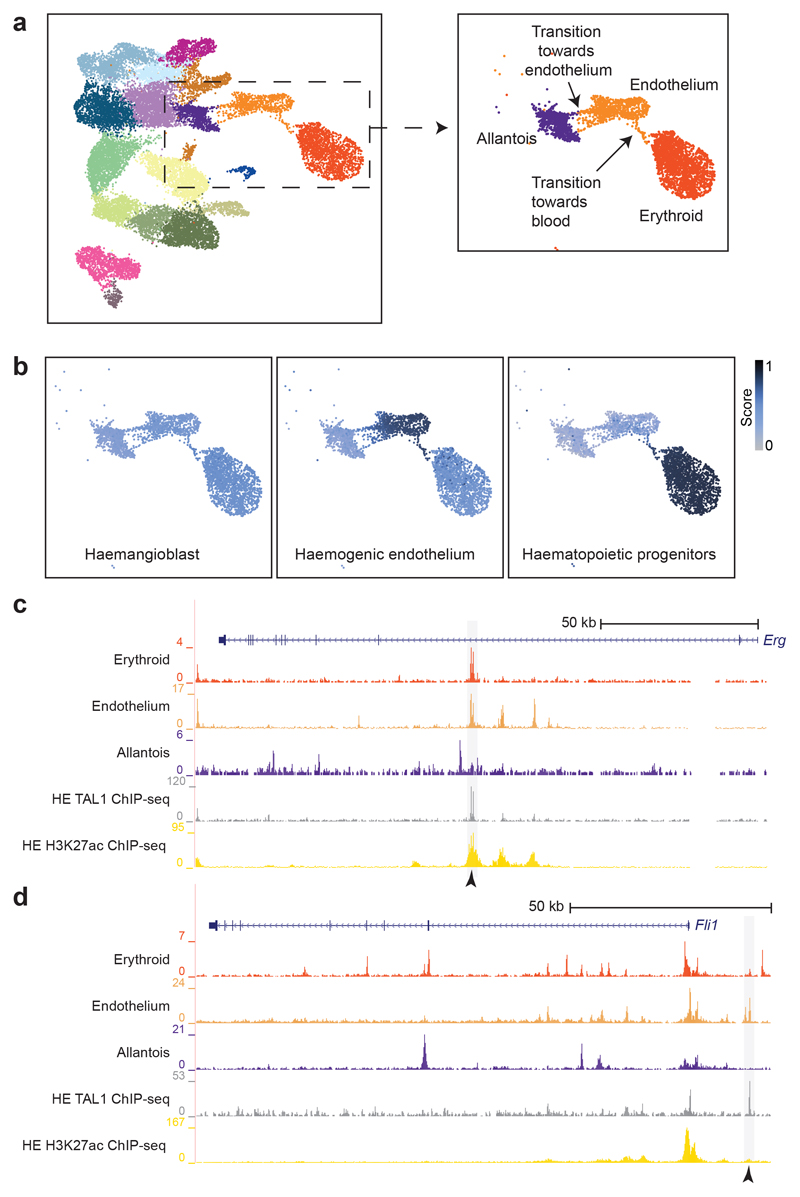
Fig. 5. Endothelial-specific sites bound by TAL1 in vitro highlight known haemato-endothelial enhancers.
a, UMAP as in Fig. 1b with a box around the allantoic-haemato-endothelial cells (left). Zoomed in UMAP (right) shows and describes the cells found in this landscape only. b, UMAP of allantoic-haemato-endothelial cells (n=3,284 cells) showing the enrichment scores (colour gradient from grey=0 to dark blue=1) for TAL1 ChIP-seq peaks obtained from in vitro-derived haemangioblasts, haemogenic endothelium and haematopoietic progenitors from32. ChIP-seq peaks were taken from http://codex.stemcells.cam.ac.uk/. c, Genome browser tracks showing the Erg (top) and the Fli1 (bottom) loci. Black arrowheads indicate the Erg +85kb (top) and the Fli1 -15kb (bottom) enhancers. Tracks correspond to the snATAC-seq profiles of the erythroid, endothelium and allantois cell types after cell pooling, the TAL1 ChIP-seq for haemogenic endothelial cells (“TAL1 ChIP-seq HE”, grey) and H3K27ac ChIP-seq for haemogenic endothelial cells from32 (“H3K27ac HE”, gold). Haemogenic endothelial TAL1 and H3K27ac ChIP-seq tracks were obtained from http://codex.stemcells.cam.ac.uk/.