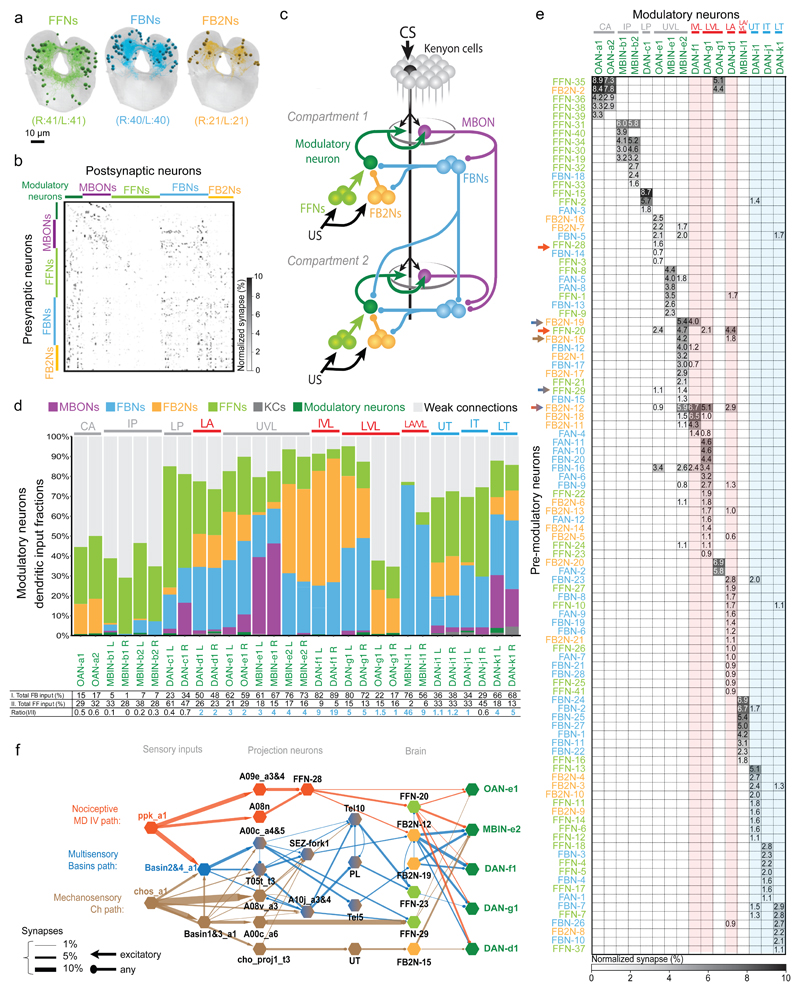
Figure 2. Comprehensive EM reconstruction of pre-modulatory neurons reveals a multilayered recurrent architecture for regulating learning.
a Projections of EM reconstructions of 102 neuron pairs found to be strongly connected to modulatory neurons. The majority (61) relays inputs from MBONs: 40 FBNs pairs (light blue) ; and 21 FB2Ns (yellow). The remaining 41 are classified as FFNs (light green).
b Connectivity matrix showing normalized synaptic input (in %) each homologous pair of postsynaptic (columns) neurons receives from each pair of presynaptic (rows) neurons.
c Schematic wiring diagram of the Extended MB circuit.
d Fraction of total dendritic input each modulatory neuron receives from different neuron types. Most DANs receive more than half of their input from MBON feedback pathways, whereas most OANs receive most input from weakly connected partners. Some DANs extend dendritic arbors to the KCs which accounts for KCs dendritic input; KCs axonic inputs are described elsewhere (Eichler et al. 2017). Red and blue, aversive and appetitive memory compartments, respectively, in all legends.
Bottom: Percent of inputs onto modulatory neurons from (I.) MBON, FBN, and FB2N, (II.) FFNs, and their ratio. This ratio is greater than 1 in most cases.
e Connectivity matrix showing normalized synaptic input (expressed as % input) each modulatory neuron (columns) receives from each pre-modulatory neuron (rows).
Pre-modulatory neurons synapse onto a single or a few functionally related modulatory neuron(s) (See also Extended Data 3).
f US pathways converge with feedback pathways at modulatory neurons and at FB2Ns. Diagram shows the shortest identified US pathways from somatosensory neurons to vertical lobe modulatory neurons. Thickness of the arrow represents fraction of input.