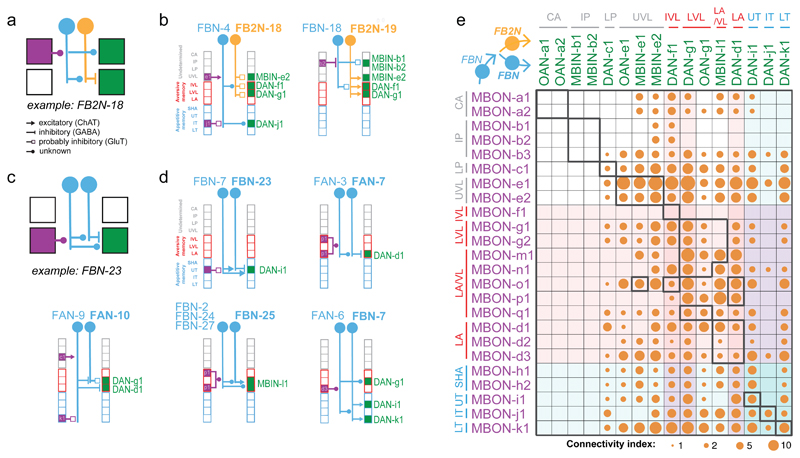
Figure 5. Two-step feedback from most MBONs to most modulatory neurons further increases inter-compartment connectivity.
a Schematic diagram of a two-step feedback motif involving an FBN (blue) and an inhibitory FB2N (yellow). The FBN provides one-step feedback to some compartments and two-step feedback to others via the FB2N. Arrowheads denote the type of synaptic connection in a-d.
b Two example two-step within-compartment feedback motifs involving FB2Ns with identified neurotransmitters.
c Schematic diagram of a two-step feedback motif involving two FBNs (blue) rather than an FBN and an FB2N. d Five example two-step within-compartment feedback motifs involving FBNs with identified neurotransmitters illustrate the diversity of two-step feedback connections.
e Most modulatory neurons receive two-step feedback from most MBONs. Connectivity matrix shows connections between MBONs and modulatory neurons via two-step feedback pathways, obtained by multiplying the MBON→FBN, FBN→FB2N/FBN and FB2N/FBN→modulatory neuron connectivity matrices. The connectivity indexes are the cubic root of the resulting matrix products.