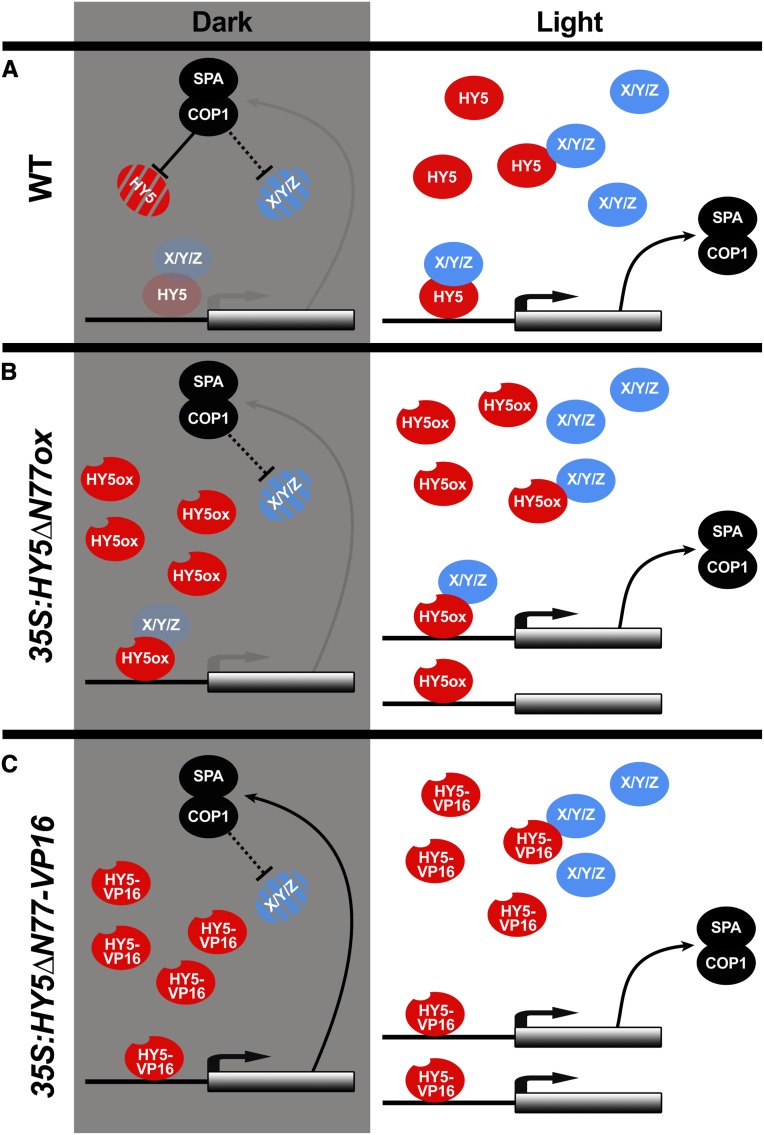
Figure 6.
A HY5-COP1/SPA Feedback Loop Is a Light-Regulated Clutch.
(A) In wild-type dark-grown seedlings, HY5 can slightly activate the expression of its target genes. These genes include members of the COP1/SPA ubiquitin ligase complex, which promote HY5 degradation. The absence of the interacting proteins (X/Y/Z) limits HY5 activity. These interacting proteins are likely light-dependent at the level of transcription or protein stability, possibly by COP1/SPA. In the light, COP1 and SPA transcription increases, but the protein complex, which promotes HY5 degradation, becomes inactive, enabling HY5 and its interacting proteins to accumulate, interact, and activate the transcription of target genes.
(B) In the dark, HY5∆N77ox cannot increase the expression of its targets, since its interaction partners cannot accumulate. As interacting proteins accumulate in the light, however, HY5∆N77ox can function normally.
(C) Overexpression of HY5∆N77-VP16 can lead to gene activation in the dark, removing the requirement for interacting proteins and decoupling HY5 function from COP1/SPA activity.
Black lines indicate strong activity, and gray lines indicate very weak activity.