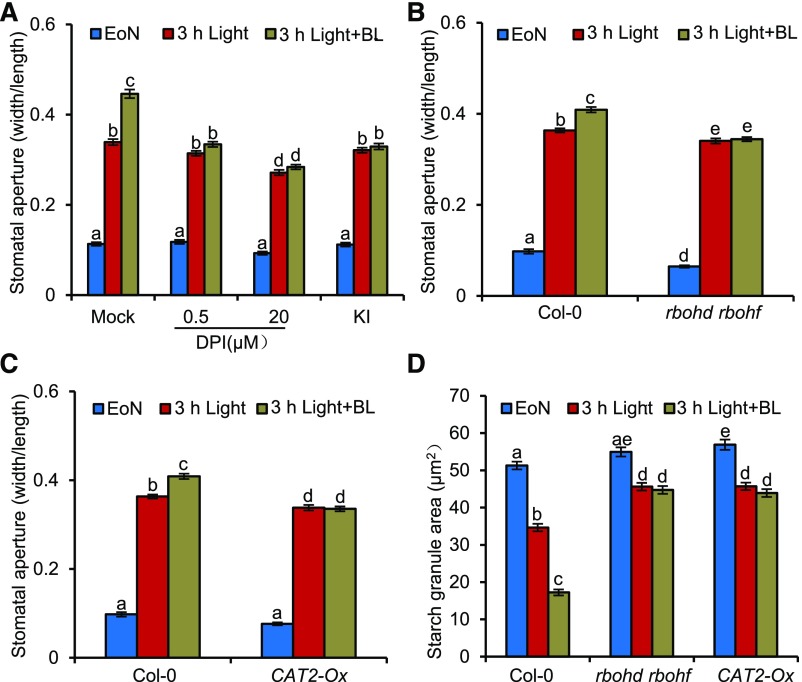
Figure 2.
H2O2 Is Required for BR-Mediated Guard Cell Starch Degradation and Stomatal Opening.
(A) DPI and KI treatment reduced the BR effects on stomatal opening. The rosette leaves of 4-week-old Col-0 were transferred to half strength MS liquid medium containing the indicated concentrations of DPI or 1 mM KI and incubated overnight in the dark. Next, 100 nM BL or 80% ethanol solution was added to the medium at the EoN and then illuminated with white light for 3 h.
(B) to (D) Quantification of stomatal aperture ([B] and [C]) and starch granules (D) in guard cells of intact leaves of the wild-type, rbohd rbohf, and CAT2-Ox plants with or without BR treatment. The rosette leaves of the 4-week-old wild-type Col-0, rbohd rbohf, and CAT2-Ox were transferred to half strength MS liquid medium and incubated overnight in the dark. Next, 100 nM BL or 80% ethanol solution was added to the medium at the EoN, and samples were illuminated with white light for 3 h.
The ratio of stomatal aperture width to length or guard cell starch granules from at least 100 guard cells from 10 to 15 leaves of eight different plants were measured using ImageJ software. Three independent biological repeats were performed. Error bars indicate sd (n = 3 biological repeats). Different letters above the bars indicate statistically significant differences between samples (two-way ANOVA followed by a post hoc Tukey test, P < 0.05).