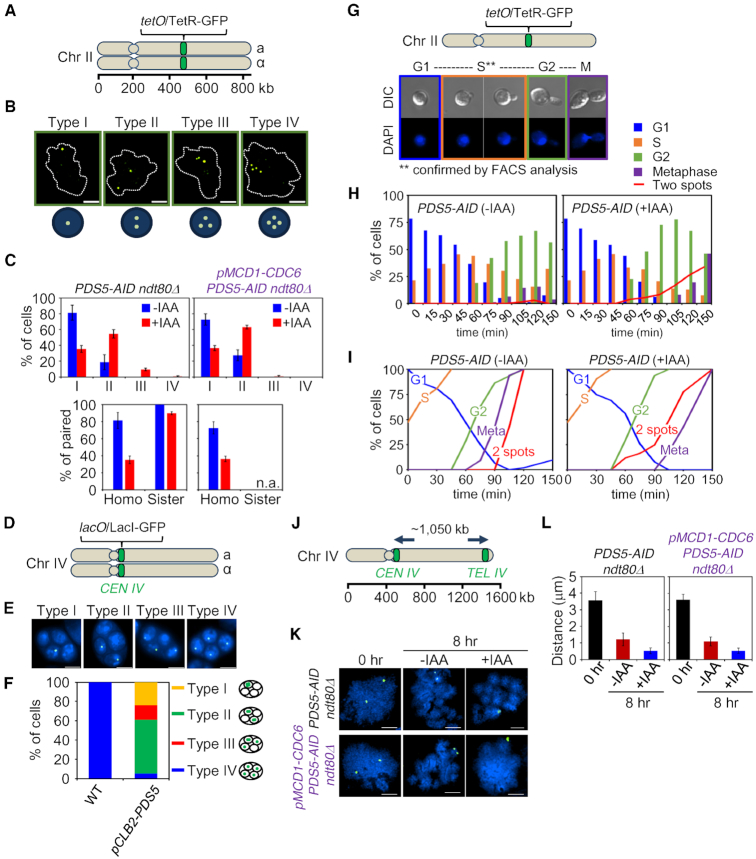
Figure 1.
In meiotic prophase, Pds5 is specifically recruited to interhomolog (versus intersister) interactions. (A) Illustration of the tet operator (tetO) and Tet repressor (TetR) array. The tet operator arrays were integrated into chromosome II at the arm region. (B) Assay for sister cohesion and homolog pairing in ndt80Δ. Cohesion and homolog pairing activity were monitored using a diploid strain homozygous for tetO/TetR-GFP at chromosome II of PDS5-AID ndt80Δ and pMCD1-CDC6 PDS5-AID ndt80Δ cells that were arrested at pachytene. Cells with nuclei of type I (one focus, paired chromosomes), type II (two foci, no pairing with sister chromatid cohesion or paired chromosomes with a cohesion defect for one sister chromatid), type III (three foci, no pairing with a cohesion defect for one sister chromatid) and type IV (four foci, no pairing with cohesion defect for two pairs of sister chromatids) are shown in representative images. Chromosome spreads were prepared and stained with anti-GFP monoclonal antibody (green) and DAPI (dot lines) dyes. The scale bar indicates 2.5 μm. (C) Analysis of TetR-GFP focus numbers per cell. Top: The percentage of each type is shown for PDS5-AID ndt80Δ (n = 450) and pMCD1-CDC6 PDS5-AID ndt80Δ (n = 605). GFP foci were analyzed in the presence or absence of auxin in whole cells at 8 h. Bottom: Pairing of homologs and pairing (cohesion) of sister chromatids. Homo, homolog pairing; Sister, sister cohesion. Auxin (2 mM) was added to induce degradation of Pds5. Error bars represent the mean ± SD. (D) Illustration of the lac operator (lacO) and Lac repressor (LacI)-GFP array on CEN4. The lacO arrays were integrated into centromere area of chromosome IV. (E) Analysis for chromosome segregation in meiosis II. Cells with four DAPI bodies were checked for the number of LacI-GFP focus in four spores. Segregation of chromosome IV was analyzed using a strain homozygous for CEN4-GFP. Type I, 4:0:0:0; type II, 2:2:0:0; type III, 1:1:2:0; type IV, 1:1:1:1. (F) Segregation of chromosome IV in meiosis II cells. Cells with four nuclei were counted for the number of GFP focus (lacO/LacI-GFP signals) in a spore (n > 100 for WT; n > 250 for pCLB2-PDS5). The main types of chromosome segregation are illustrated in the right side of the plot. (G) Top: Illustration of the tet operator (tetO) and Tet repressor (TetR) array. Bottom: Representative images of cells from G1 phase to metaphase (M). (H) Analysis of cohesion in PDS5-AID cells during progression from G1 phase to metaphase. Cells were synchronized in G1, and then auxin (2 mM) was added. The percentage of cells with two GFP-foci is plotted in the presence or absence of auxin (>100 cells were counted at each time point). (I) Cumulative curves derived from primary data in (H). (J) Analysis of the axial length of chromosome IV. Chromosome IV was marked by CEN4-GFP and TEL4-GFP signals. (K) Representative images of CEN4-GFP and TEL4-GFP signals in PDS5-AID ndt80Δ and pMCD1-CDC6 PDS5-AID ndt80Δ cells on chromosome spreads. The scale bars indicate 2.5 μm. (L) Compaction analysis of meiotic chromosome in PDS5-AID ndt80Δ and pMCD1-CDC6 PDS5-AID ndt80Δ cells. The chromosome length at pachytene was determined by measuring the distance between the two GFP foci with lacO/LacI-GFP (n > 50). Auxin (2 mM) was added to induce degradation of Pds5. Error bars represent the mean ± SD.