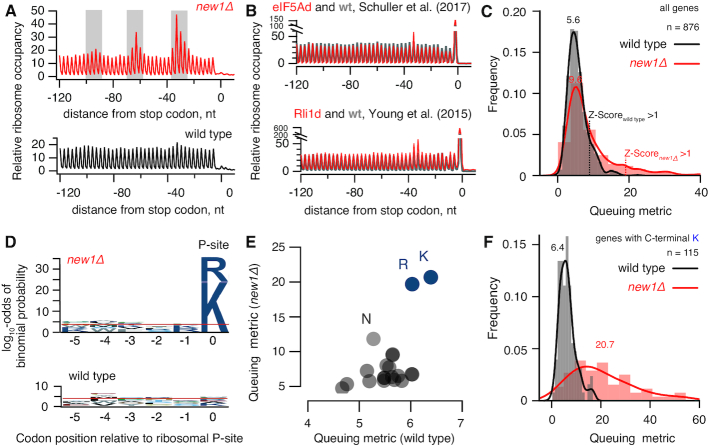
Figure 5.
Loss of New1 leads to ribosome queuing at C-terminal lysine and arginine residues. (A) Metagene analysis Ribo-Seq libraries detects ‘waves’ of the ribosomal density preceding the stop codon in the case of new1Δ but not wild-type. Note that due to technical reasons the metagene plots lack the pronounced peak at the stop codon both in the case of wild-type and new1Δ datasets. (B) Metagene analysis of Rli1-depleted and the corresponding wild-type (63) as well as eIF5A-depleted and the corresponding wild-type (62) Ribo-Seq datasets. (C) ‘3′-terminal ribosome queuing metric’ (or just ‘queuing metric’ for short) computed for individual ORFs. (D) Sequence conservation analysis for ORFs displaying high degree of ribosomal queuing at the C-terminus (Z-score cut-off of 1) in wild-type and new1Δ. Over-representation of specific amino acids at positions relative to the P-site codon was computed using pLogo (67). Horizontal red lines represent significance threshold (the log10-odds 3.45) corresponding to a Bonferroni corrected P-value of 0.05. (E) Mean ribosome queuing distribution for ORFs in wild-type and new1Δ sorted by the nature of the C-terminal amino acid. (F) Ribosome queuing metric distribution for genes with C-terminal lysine. All analyses were performed using pooled datasets collected at 20°C. Analyses of individual replicates of both 20°C and 30°C datasets are presented on Supplementary Figure S9C–F.