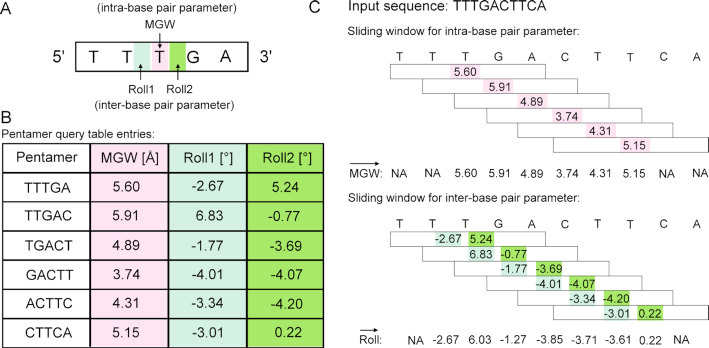
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the pentamer model for high-throughput prediction of DNA shape. (A) A pentamer model was used to characterize and predict DNA shape features for either one intra-base pair parameter (e.g. MGW, in pink) or two inter-base pair parameters (e.g. Roll, in light and dark green). The intra-base pair parameter specifies the relative location of the bases within a base pair, or in the case of MGW is defined with respect to a base-pair plane, while the inter-base pair parameter indicates the relative location of two adjacent base pairs, or refers to a base-pair step (24). (B) A sliding-pentamer window was used to mine the prediction results from MC simulations and, in turn, generate a query table of average DNA shape features of each pentamer (45). (C) The pentamer query table integrated with a sliding-pentamer window can be used to predict shape features for a given DNA sequence of any length in a high-throughput manner. For predicting intra-base pair parameters (e.g. MGW), each sliding step assigns a shape prediction for the central base pair. For predicting inter-base pair parameters (e.g. Roll), each sliding step assigns a shape prediction for two central base-pair steps. The overlapping values arising from two adjacent pentamers at the same nucleotide position will then be averaged. The sliding-window approach will result in a feature vector (12).