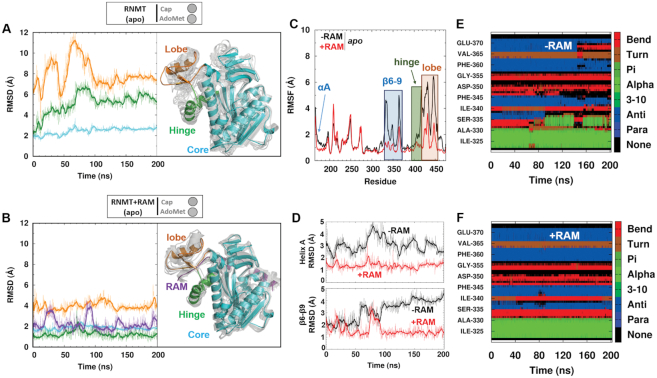
Figure 4.
Modulation of RNMT stability by RAM. (A and B) Left: Time evolution of the backbone atoms RMSD (in Å) of key structural elements of RNMT during the aMD simulation of apo-RNMT in the absence (A) and presence (B) of RAM. Right: A representative snapshot of apo-RNMT in the absence (A) and presence (B) of RAM displaying the key structural elements: catalytic core (cyan), hinge (green) and lobe (orange) regions. The representative snapshot is superimposed with multiple structures (light grey) that were sampled from the entire aMD trajectory and illustrate the range of conformational dynamics in each system. (C) The backbone RMSFs (in Å) of the catalytic domain of RNMT (residues 165–475) computed from the aMD simulation of apo-RNMT in the absence (black) and presence (red) of RAM. (D) Time evolution of the backbone RMSD (in Å) of α-helix A and strands β6–9 during the aMD simulation of apo-RNMT in the absence (black) and presence (red) of RAM. (E and F) Secondary structure analysis of the β-strand ‘lid’ region of RNMT (residues 320–375) performed on the aMD trajectories of apo-RNMT in the absence (E) and presence (F) of RAM.