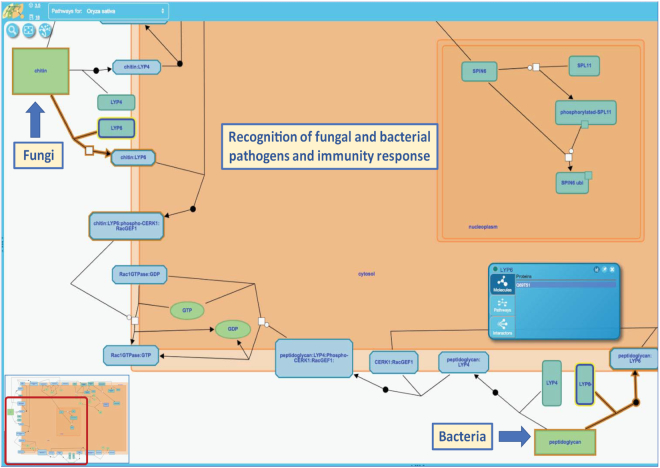
Figure 2.
An example of a pathway depicting biotic stress response in rice. Current knowledge related to ‘Recognition of fungal and bacterial pathogens and immunity response’ has been summarized in this pathway. Depending on the type of pathogen, components of the microbial cell walls (e.g. fungal chitin, or bacterial peptidoglycan) serve as elicitors in plant innate immunity. The chitin elicitor binding protein (CEBiP) acts as the chitin receptor, whereas membrane-localized lysin motif-containing proteins 4 and 6 (LYP4 and LYP6) bind to peptidoglycan and chitin. Eventually, the binding of microbial cell wall components to plant cell membrane receptor(s) induces a downstream signaling cascade, which in turn triggers expression of regulatory factors, defense-related genes, and the components of programmed cell death leading to pathogen resistance. View pathway at https://plantreactome.gramene.org/PathwayBrowser/#/R-OSA-9611432