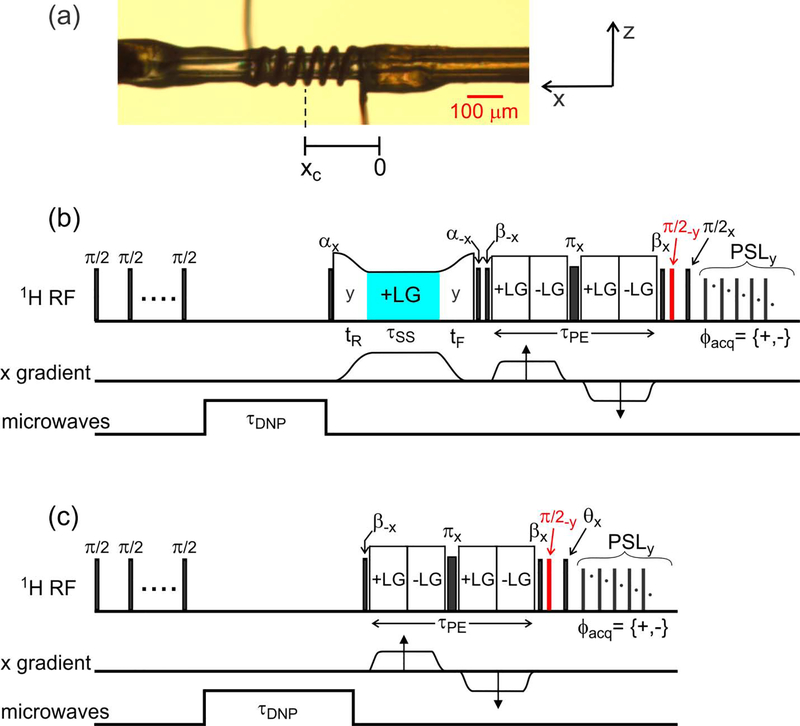
Figure 1:
(a) Photograph of the microcapillary that contains the sample in these experiments, with the RF microcoil wound around the microcapillary. The microcoil is displaced by xc ≈ 200 μm from the center of the x gradient coil. (b) Pulse sequence used to acquire 1D images with slice selection. After a train of π/2 pulses to destroy pre-existing 1H magnetization, magnetization is created by microwave irradiation for τDNP = 0.5 s. As described in the text, slice selection is carried out by RF phase modulation (on alternate scans) during a Lee-Goldburg (LG) irradiation period that is sandwiched between pulses with flip angles α = 125.3°. The phase modulation period is highlighted in cyan. Phase-encoded imaging occurs in period τPE, and 1H NMR signals are detected during pulsed spin-locking (PSL), consisting of a train of pulses with 60° flip angles. Imaginary parts of phase-encoded signals are detected by applying the π/2 pulse shown in red. (c) Pulse sequence for imaging the RF amplitude as a function of x. The flip angle θ and the x gradient amplitude during τPE are incremented independently to generate a 2D data set.