Figure 20. Loss of CTNNA1 and CLDN4 loss in endoneurial microvessels in the sural nerve of a patient with vasculitic neuropathy with chronic neuropathic pain.
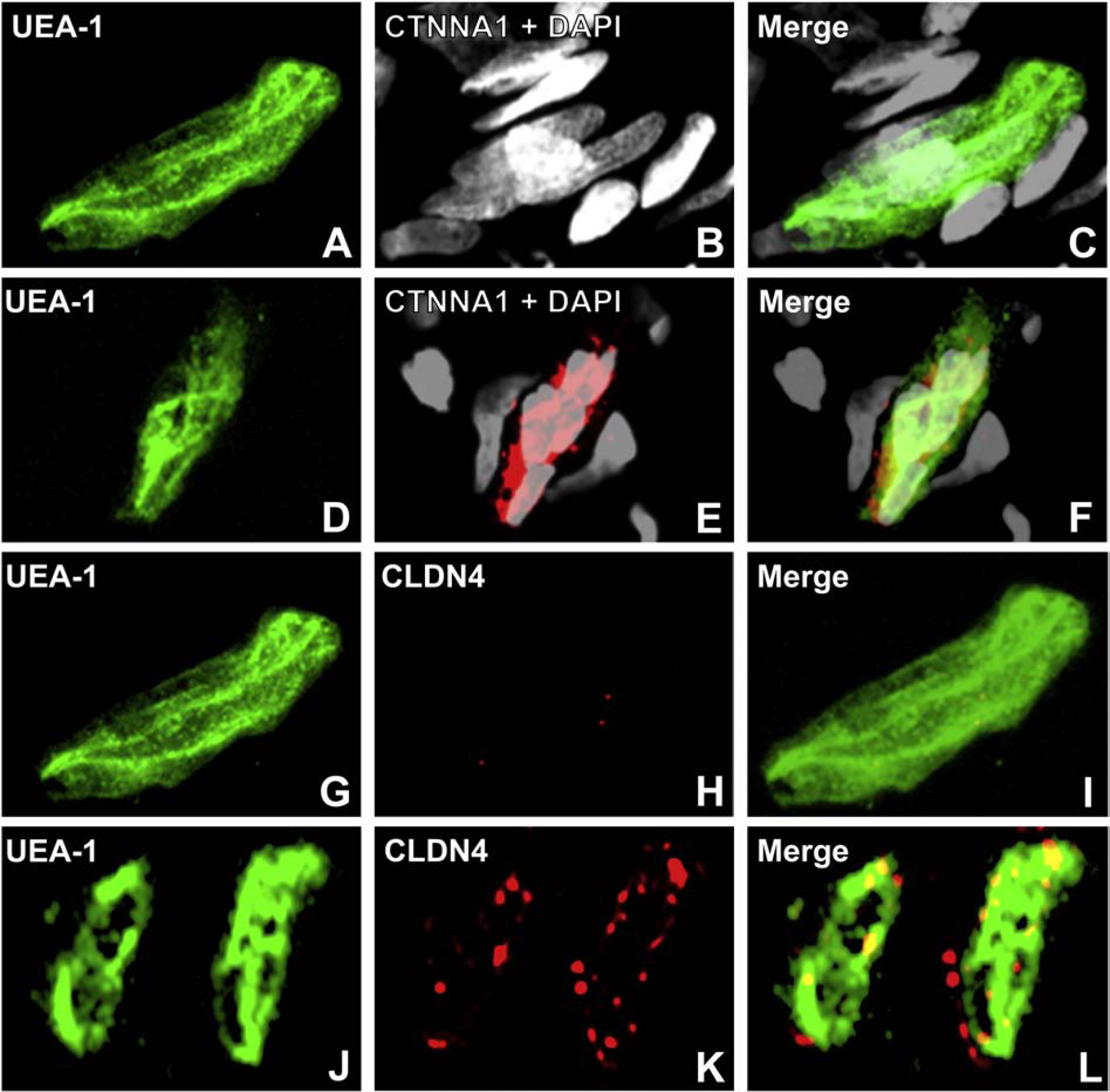
Digital high resolution indirect immunohistochemistry confocal micrographs of endoneurial microvessels from a patient with a vasculitic neuropathy and chronic neuropathic pain and age- and sex-matched normal adult control sural nerves stained with UEA-1 to detect endothelial cell membranes (green; A, D, G and J), and junctional complex molecules CTNNA1 (red, with nuclei stained with DAPI, pseudocolor grey, B and E) or CLDN4 (red, H and K), show loss of both endoneurial microvessel CTNNA1 (B and C) and CLDN4 (H and I) expression compared to the plaque-like linear CTNNA1 (E and F) and punctate CLDN4 (K and L, consistent with a tight junction protein) associated with normal endoneurial endothelial microvessel membranes. This observation suggests that molecular alterations of essential junctional complex proteins may occur in vasculitic neuropathy in association with chronic neuropathic pain.
