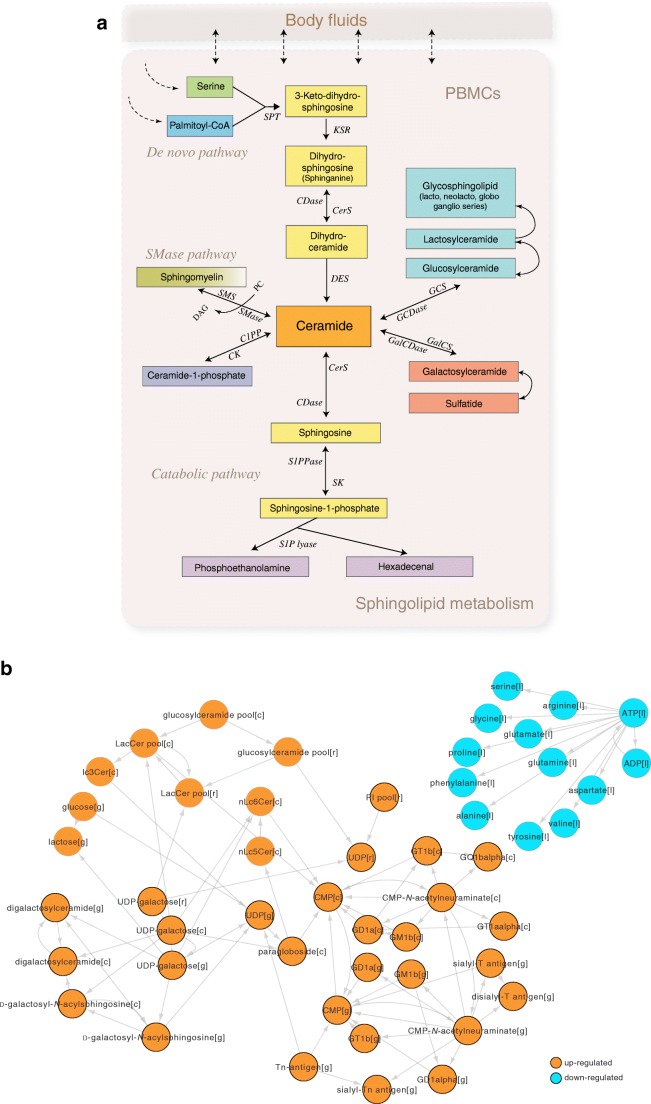
Fig. 5.
Regulation of sphingomyelin pathways in progression to islet autoimmunity and overt type 1 diabetes. (a) Canonical pathways of sphingolipid metabolism in humans. C1PP/C1PPase, ceramide-1-phosphate phosphatase; CDase, ceramidases; CerS, ceramide synthase; CK, ceramide kinase; DAG, diacylglycerol; DES, dihydroceramide desaturase; GalCDase, galactosidase; GalCS, galatosylceramide synthase; GCDase, glucosidase; GCS, glucosylceramide synthase; KSR, 3-keto dihydrosphinganine reductase; PC, phosphatidylcholine; S1P lyase, sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase; S1PPase, sphingosine phosphate phosphatases; SK, sphingosine kinase; SMase, sphingomyelinase; SMS, sphingomyelin synthetase; SPT, serine palmitoyl-CoA transferase. (b) RMs predicted for PBMCs that were significantly different (false discovery rate [FDR] <0.05) between PT1D and P1Ab groups. The orange and cyan colours denote up- and downregulation of the RMs, respectively. The cellular compartments ‘[c]’, ‘[g]’, [r]’, ‘[l]’ denote the cytosol, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum and lysosome, respectively