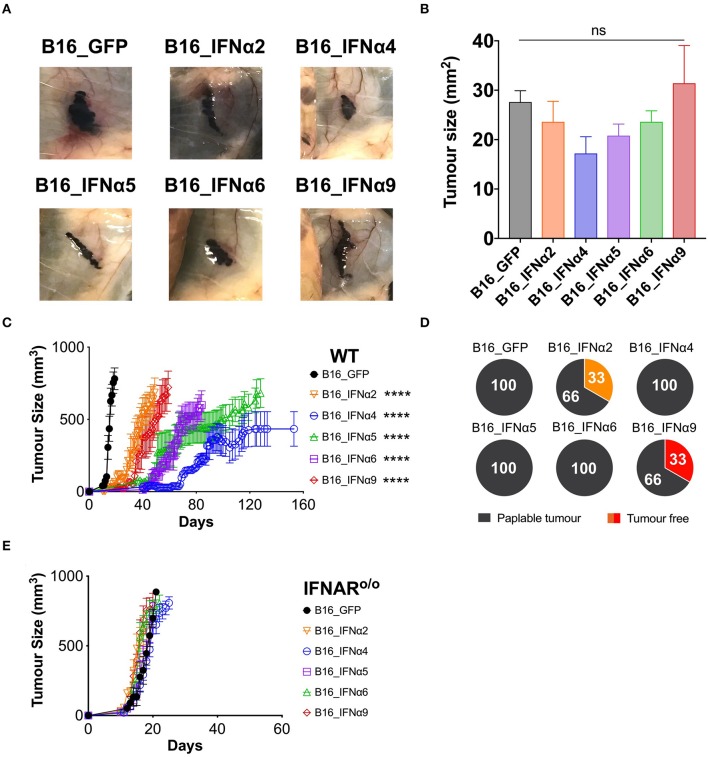
Figure 2.
IFNα subtypes significantly delay tumor growth in WT mice. WT mice were inoculated subcutaneously with 5 × 105 B16_GFP or B16_IFNα cells. (A) Representative images of subcutaneous tumors 8 days post-tumor inoculation (n = 5 per group). (B) Tumor area of B16 tumors (mean ± SEM) harvested 8 days post-tumor inoculation (n = 5 per group). (C) Tumor growth was measured over time. Each point signifies mean ± SEM combined from four independent experiments (n = 10–18 per group). (D) Proportions of WT mice that developed palpable tumors over time from four independent experiments (n = 10–18 per group). (E) IFNAR o/o mice were inoculated subcutaneously with 5 × 105 B16_GFP or B16_IFNα cells. Tumor growth was measured over time. Each point signifies mean ± SEM from two independent experiments (n = 10–12 per group). Tumor growth curves of B16_GFP vs. each B16_IFNα were compared using repeated-measure two-way ANOVA (mixed-model) followed by the Bonferroni post hoc test, ****p < 0.0001.