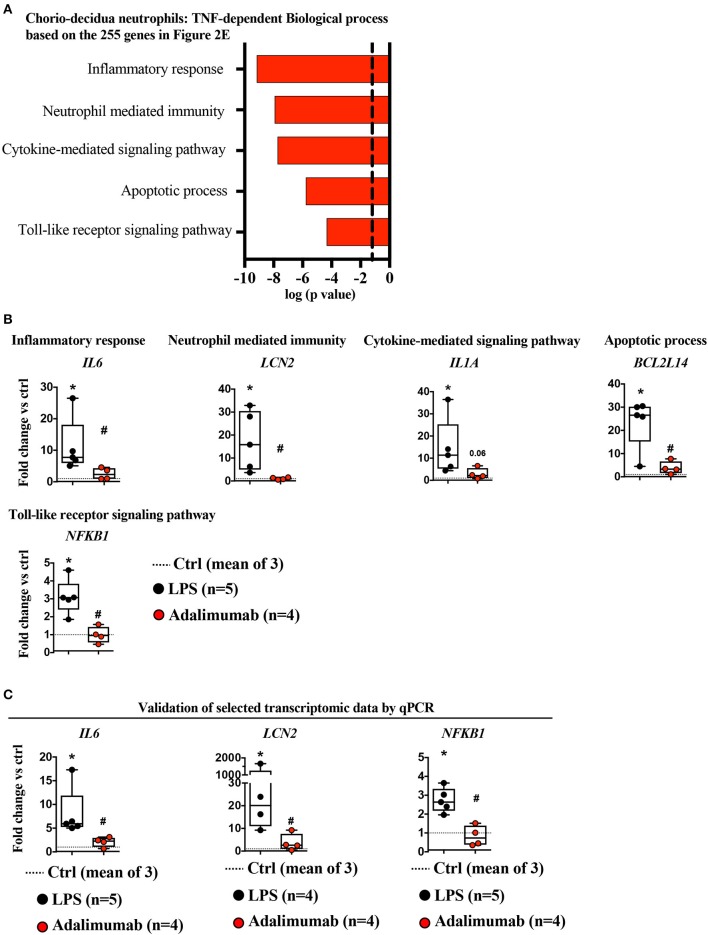
Figure 3.
TNF-signaling inhibition decreased neutrophil mediated immunity. (A) Biological processes of LPS-induced genes (≥4-fold vs. controls) that were significantly down-regulated by Adalimumab (≥1.5-fold decrease vs. LPS) designated as “TNF-dependent genes,” determined using Enrichr. Dotted line represents gene-expression values representing the mean of three control animals. (B) Representative genes representing biological processes inhibited by Adalimumab shown in (A) (dotted-line represents the mean of 3 Ctrl; LPS n = 5; Adalimumab n = 4). (C) Validation of selected transcript expression by qPCR analysis. mRNAs were isolated from FACS-sorted chorio-decidua neutrophils from Ctrl (dotted-line represents the mean of 3 Ctrl), LPS- (n = 4–5), and Adalimumab-treated animals (n = 4). qPCR was performed using rhesus-specific Taqman probes. The values were first internally normalized to the endogenous 18S RNA. For each gene, the box plot (median and 5–95th percentile and outliers) shows fold-change of gene expression in chorio-decidua neutrophils normalized to control chorio-decidua neutrophils (dotted-line represents the mean of 3 ctrl). *p < 0.05 vs. ctrl; #p < 0.05 vs. LPS (Mann–Whitney U-test).