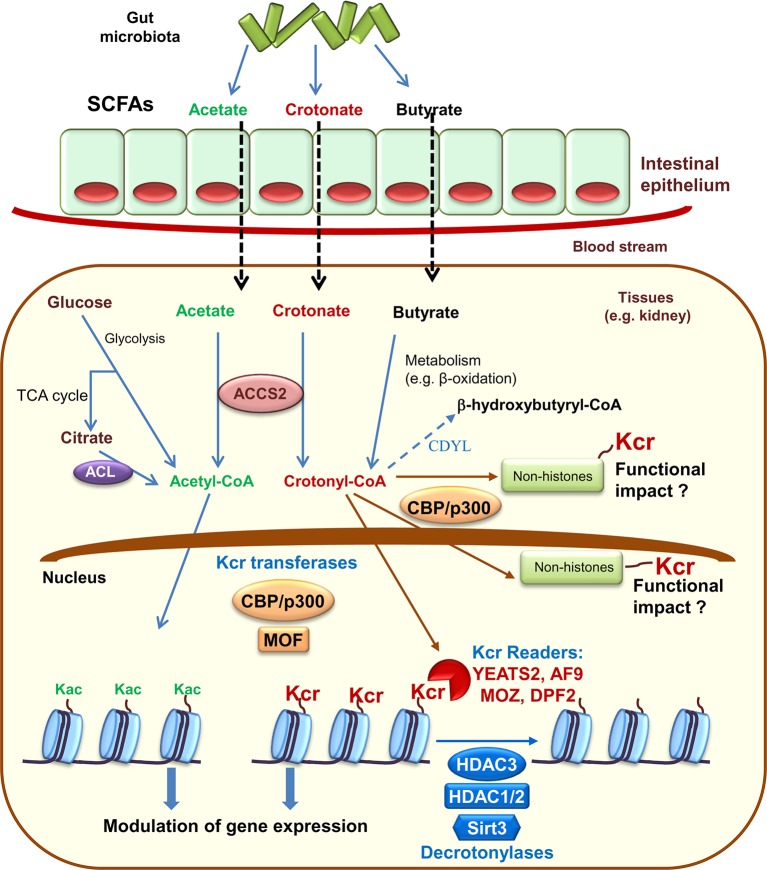
Figure 1.
Histone crotonylation: enzymes and modulators. The gut microbiota is a source of short chain fatty acids (SCFAs) that inside cells may be metabolized to acetyl-CoA or crotonyl-CoA. These are the precursors that enzymes may use to promote lysine acetylation (Kac) or lysine crotonylation (Kcr) of histone and non-histone proteins. Crotonylated proteins have now been found within the nucleus and the cytoplasm. Already characterized crotonyltransferases (also termed crotonylases) include CBP/P300 and MOF, while histone decrotonylases include some histone deacetylases (HDAC) and sirtuin 3 (Sirt3). Kcr readers, proteins that identify Kcr in histones, include YEATS domain human proteins YEATS2 and AF9 as well as DPF family proteins MOZ and DPF2. Chromodomain Y-like (CDYL) negatively regulates histone crotonylation acting as a crotonyl-CoA hydratase that converts crotonyl-CoA required for Kcr into β-hydroxybutyryl-CoA. TCA, tricarboxylic acid; ACL, ATP citrate lyase; ACCS2, acyl-CoA Synthetase Short Chain Family Member 2.