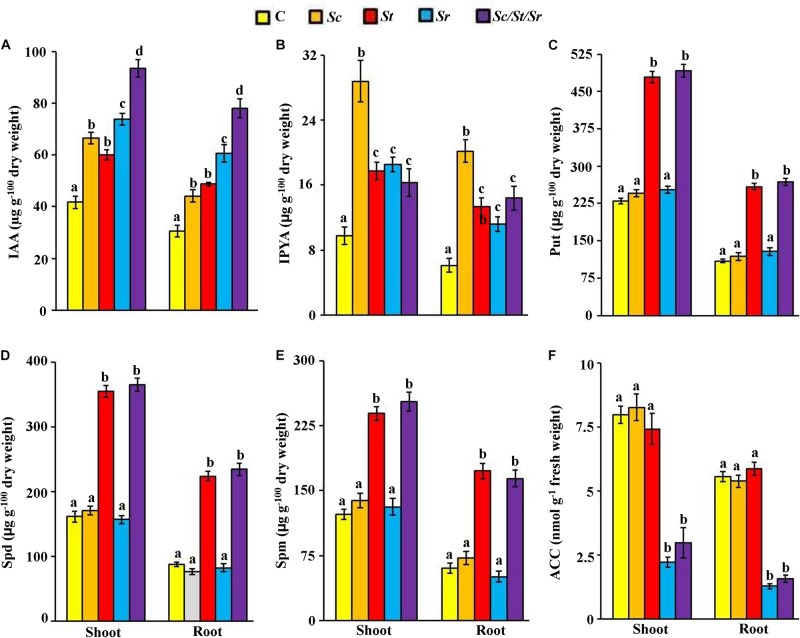
FIGURE 6.
Effect of the individual and/or consortium of the rhizosphere-competent actinobacteria on endogenous auxins, polyamines and ACC content of Salicornia bigelovii. Endogenous contents of (A) IAA; (B) IPYA; (C) Put; (D) Spd; (E) Spm, and (F) ACC in S. bigelovii shoot and root tissues after treatment with autoclaved non-inoculated oat bran (control); auxin-producing isolate #21 (S. chartreusis UAE1, Sc); polyamine-producing isolate #7 (S. tritolerans RAK1, St); ACCD-producing isolate #11 (S. rochei RAMS1, Sr); consortium of the three rhizosphere-competent isolates (Sc/St/Sr). S. bigelovii seedlings were grown in an evaporative-cooled greenhouse and maintained at 25 ± 2°C. Values are means of eight replicates for each sampling from two independent experiments. Mean values followed by different letters are significantly (P < 0.05) different from each other according to Fisher’s Protected LSD Test. Bars represent standard error. Endogenous contents of IAA, IPYA, Put, Spd, Spm, and ACC were measured at 12 wps the seeds of S. bigelovii. IAA, indole-3-acetic acid; IPYA, indole-3-pyruvic acid; Put, putrescine; Spd, spermidine, Spm, spermine; ACC, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic; ACCD, ACC deaminase; wps, weeks post-sowing.