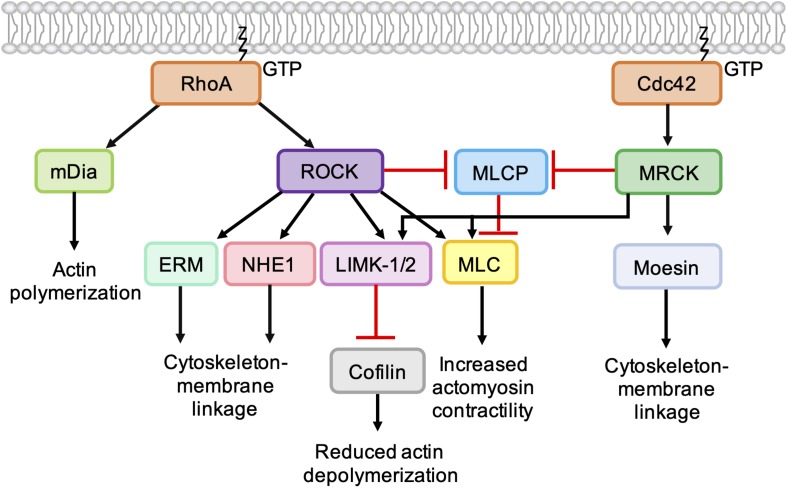
FIGURE 5.
Role of Cdc42-MRCK signaling and RhoA-ROCK signaling in regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. RhoA directly binds and activates the formin mDia, which nucleates the formation of unbranched actin filaments. ROCK activation downstream of RhoA leads to phosphorylation of LIMK-1 and LIMK-2, which phosphorylate and inactivate cofilin, leading to a reduction in actin depolymerization. ROCK activation leads to an increase in actomyosin contractility via phosphorylation of myosin light chain (MLC) and inhibition of myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP). ROCK also phosphorylates ERM proteins (ezrin, radixin, and moesin) and NHE1 (Na+/H+ -Exchanger 1) to enhance coupling of the actin cytoskeleton to integral membrane proteins. Like ROCK, MRCK activation leads to decreased actin depolymerization via phosphorylation LIMK-1 and LIMK-2 and increased actomyosin contractility via MLC phosphorylation. Phosphorylation of moesin by MRCKα may enhance coupling of the actin cytoskeleton to integral membrane proteins.