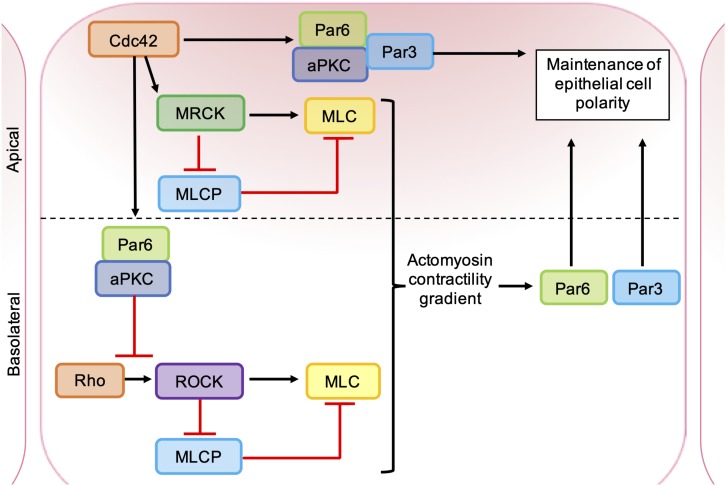
FIGURE 6.
Roles of ROCK, MRCK, and aPKC in the maintenance of epithelial cell polarity. Apical MRCK activation by Cdc42 leading to a local increase in actomyosin contractility, via phosphorylation of myosin light chain (MLC) and inhibition of myosin light chain phosphatase (MLCP). Cdc42 stimulates a Par-aPKC complex, which inhibits junctional Rho-ROCK signaling and establishes an intracellular actomyosin contractility gradient, leading to the segregation of Par proteins into distinct cellular domains. Apical GTP-bound Cdc42 binds to Par6, which in turn binds aPKC and Par3. Activation of aPKC leads to the phosphorylation of key polarity proteins that maintain apical-basal cell polarity.