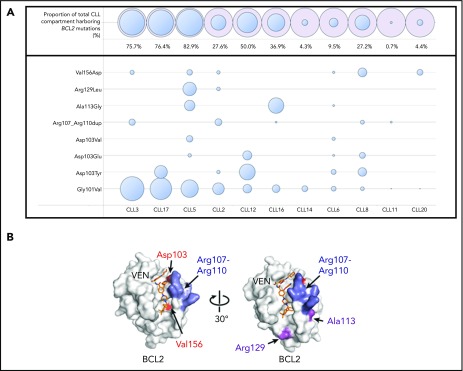
Figure 1.
BCL2 mutations in patients with progressive CLL on venetoclax. (A) BCL2 mutations in a cohort of patients with CLL progression on venetoclax. Patients are ordered in descending Gly101Val cancer cell fraction (CCF). CCF was determined as (VAF/disease burden determined by flow cytometry) × 2 (assuming heterozygosity). Area of blue circles is proportional to CCF mutated. The top row shows the total CCF harboring BCL2 mutations (the sum of individual CCF and assumes occurrence in mutually exclusive cells). Mutations detected were c.302G>T, p.(Gly101Val); c.302_303delinsTT, p.(Gly101Val); c.307G>T, p.(Asp103Tyr); c.308A>T, p.(Asp103Val); c.309C>A, p.(Asp103Glu); c.319_330dup, p.(Arg107_Arg110dup); c.338C>G, p.(Ala113Gly); c.386G>T, p.(Arg129Leu); c.467T>A, p.(Val156Asp); BCL2 NM_000633.2. Patient CLL6 had both a c.302G>T and a complex variant (c.302_303delinsTT) leading to a p.(Gly101Val) in different reads; the Gly101Val area is the sum of the 2 CCFs for this patient. (B) Structure of BCL2 protein with venetoclax bound (PDB ID 6O0K) illustrating the positions of the mutated residues Asp103, Val156, Arg107 to Arg110, Ala113, and Arg129.