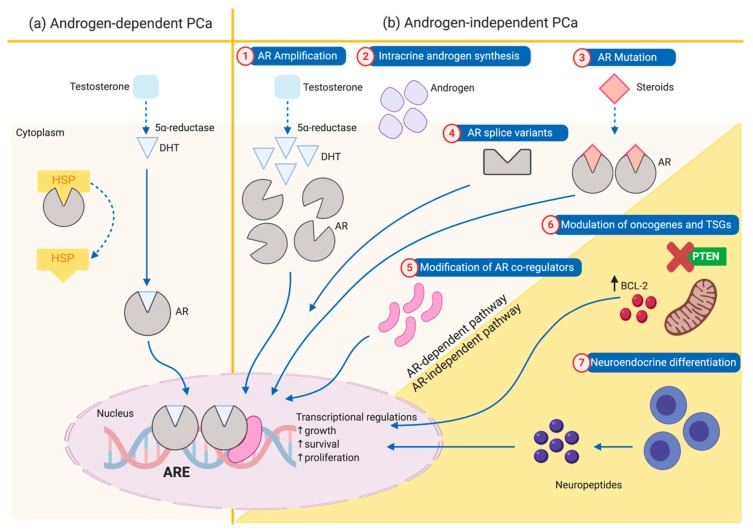
Figure 1.
Molecular mechanisms of (a) androgen-dependent PCa (ADPC) and (b) development of androgen-independent prostate cancer (AIPC). The mechanism of the development of AIPC has been categorised based on AR-dependent that involving AR which include; (1) AR amplification, (2) intracrine androgen synthesis, (3) AR mutation, (4) AR splice variants and (5) modulation of AR co-regulators, (6) modulation of oncogenes and TSGs and (7) neuroendocrine differentiation. TSGs: Tumour suppressor genes; HSP: heat shock proteins; ARE: androgen response element; DHT: dihydrotestosterone; PTEN: phosphatase and tensin homologue deleted on chromosome-10.