Figure 1.
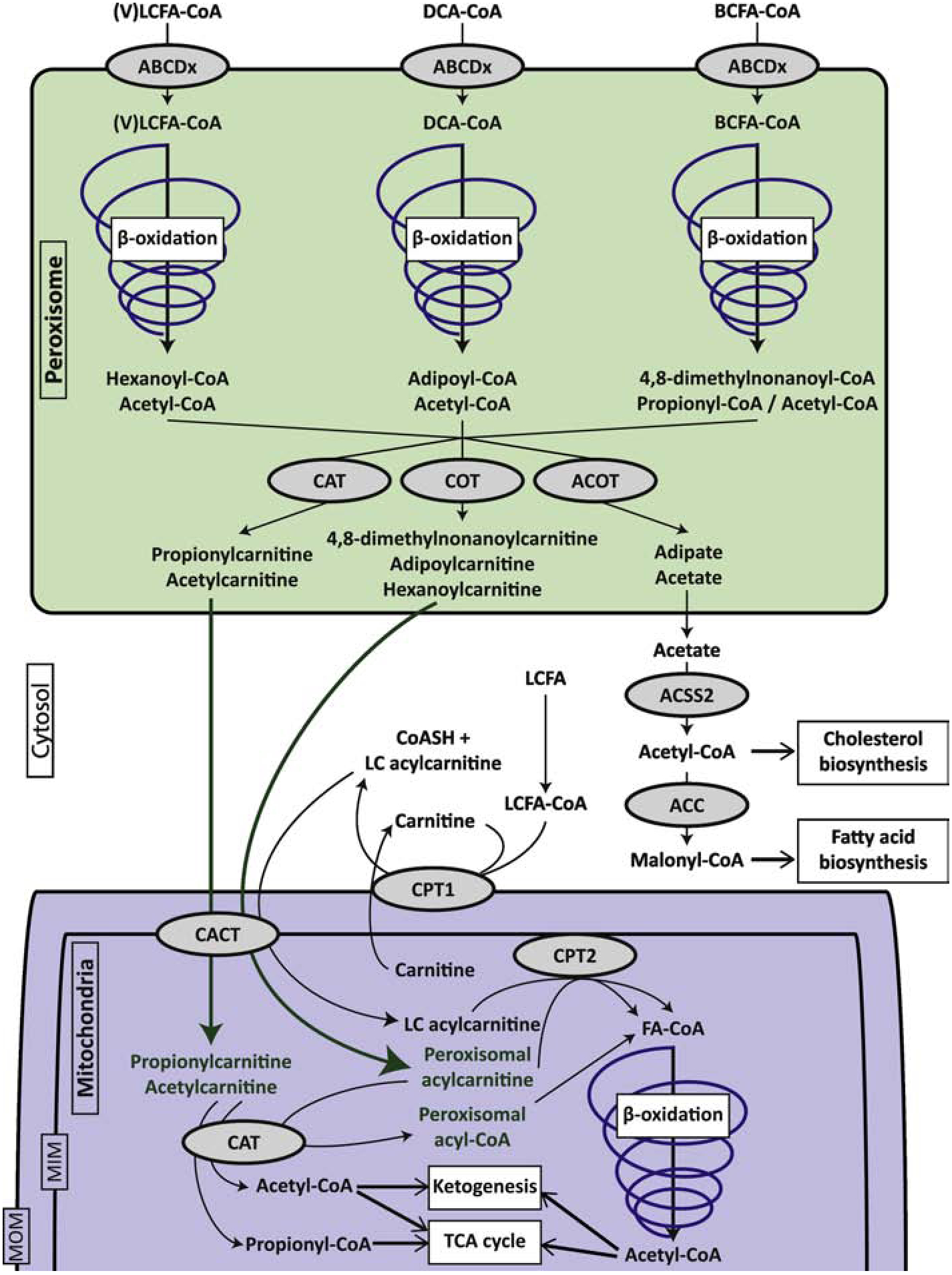
Schematic representation of acylcarnitine metabolism and transport from peroxisomes to mitochondria. The figure is focused on the substrates and products of peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation, but only the most abundant end-products are indicated. Details of the pathways and the individual enzyme steps are omitted. ABCD transporters are half-transporters and function as homodimers or heterodimers. For the simplicity of the figure, they have been represented as monomers. Abbreviations: ABCDx, members of the peroxisomal ABC transporter family; ACC, acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACSS, short-chain acyl-CoA synthetase; ACOT, acyl-CoA thioesterases; BCFA, branched-chain fatty acid; CACT, carnitine acylcarnitine translocase (SLC25A20); CPT1, carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1; CPT2; carnitine palmitoyltransferase 2; DCA, dicarboxylic acid; LCFA, long-chain fatty acid; MIM, mitochondrial inner membrane; MOM, mitochondrial outer membrane; VLCFA, very long-chain fatty acid.
