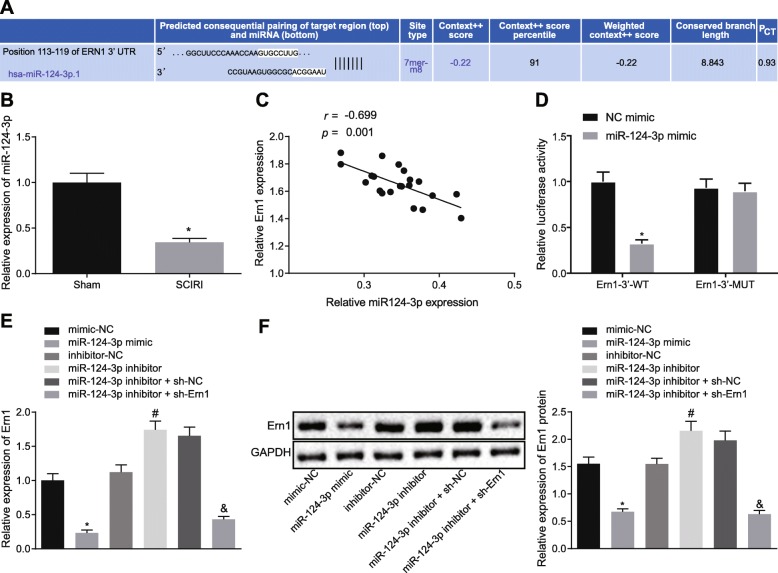
Fig. 3.
Ern1 was targeted by miR-124-3p. a Possible target genes of miR-124-3p predicted by bioinformatic analysis. b Expression of miR-124-3p in SCIRI tissues detected by RT-qPCR, *p < 0.05 versus sham operation. c Correlation between miR-124-3p and Ern1 expression in spinal cord tissues. d Dual-luciferase activity detection. e Ern1 expression in macrophage cells transfected with different plasmids determined by RT-qPCR. f Ern1 expression in differently treated macrophages measured by western blot analysis. Difference between two experimental groups conforming to normal distribution was analyzed by unpaired t-test. Comparison between two groups was analyzed by independent-sample t-test. Correlation between X-axis and Y-axis values was analyzed by Pearson’s correlation coefficient. In Fig. d, *p < 0.05 versus NC mimic. In e and f, *p < 0.05 versus NC mimic; #p < 0.05 versus inhibitor treatment; &p < 0.05 versus miR-124-3p inhibitor with shRNA versus NC. The measurement data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Unpaired t-test was used to compare two experimental groups (n = 10); one-way ANOVA was utilized to analyze differences between multiple groups with Tukey’s post hoc test; correlation between miR-124-3p and Ern1 was analyzed by Pearson’s correlation coefficient. The experiment was repeated three times