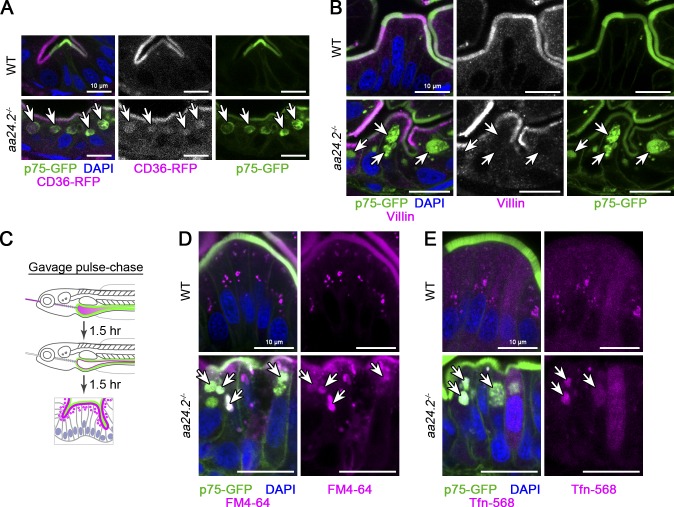
Figure S3.
Characterization of apical trafficking phenotypes in V-ATPase mutants. (A) aa24.2pd1209 mutants retain apical membrane proteins p75-GFP and CD36-RFP (arrows). TgBAC(cd36-RFP)pd1203 expresses CD36-RFP at low levels in the gut, indicating that trafficking defects are not dependent on expression levels. n > 10 mutants in two independent experiments. (B) aa24.2pd1209 mutant vacuoles (arrows) do not contain MV marker villin. n > 10 mutants in two independent experiments. (C) Experimental pulse-chase strategy for delivering soluble cargo to the apical surface of intestinal epithelial cells. 5-dpf larvae were gavaged with endocytic tracers and phenol red to visualize the intestinal lumen. After 1.5 h, the intestinal lumen was flushed out by gavage of excess unlabeled buffer containing no phenol red to visualize clearing of the intestine. (D and E) Internalized fluid phase FM4-64 (D) and receptor-mediated transferrin-AF568 (E) endocytic cargo accumulates in apical vacuoles (arrows) of aa24.2pd1209 mutants. Scale bars are 10 µm. n ≥ 4 mutants per condition for D and E.