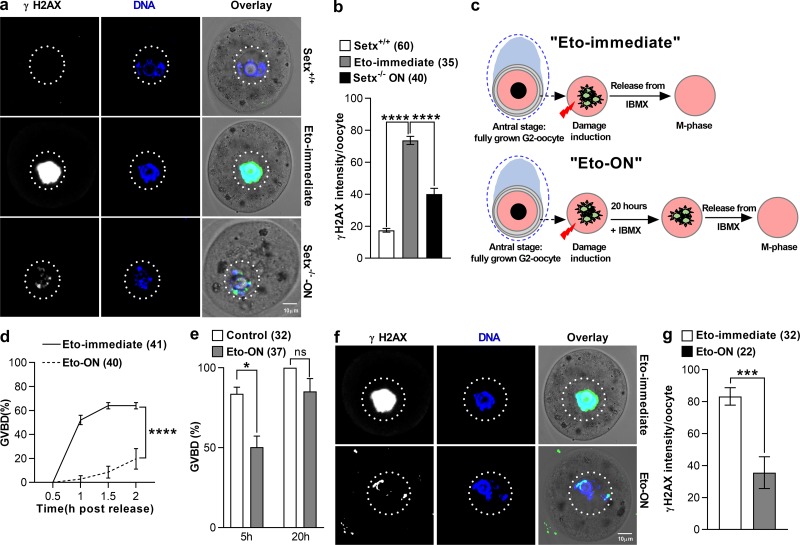
Figure 3.
Chemotherapy-induced DNA damage induces G2 arrest after a delay. (a and b) Representative images of γH2AX and DNA labeling (a) and quantification of γH2AX intensity (b) in Setx+/+ (untreated), Setx+/+ oocytes immediately after treatment with Eto (Eto-immediate), and Setx−/−-ON oocytes. (c) Schematic depicting experimental models of “Eto-immediate” and “Eto-ON” oocytes. (d) GVBD rates for Eto-immediate and Eto-ON oocytes. (e) GVBD rates 5 and 20 h after release from IBMX for DMSO-treated control and Eto-ON oocytes. (f and g) Representative images of γH2AX and DNA labeling (f) and quantification of γH2AX intensity (g) in Eto-immediate and Eto-ON oocytes. Oocyte numbers are shown in parentheses from a minimum of three independent experiments. Error bars are mean ± SEM. Two-tailed Student’s t test (b, e, and g) or two-way ANOVA (d) was used for statistical analysis. ns, P > 0.05; *, P < 0.05; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.