Figure 4.
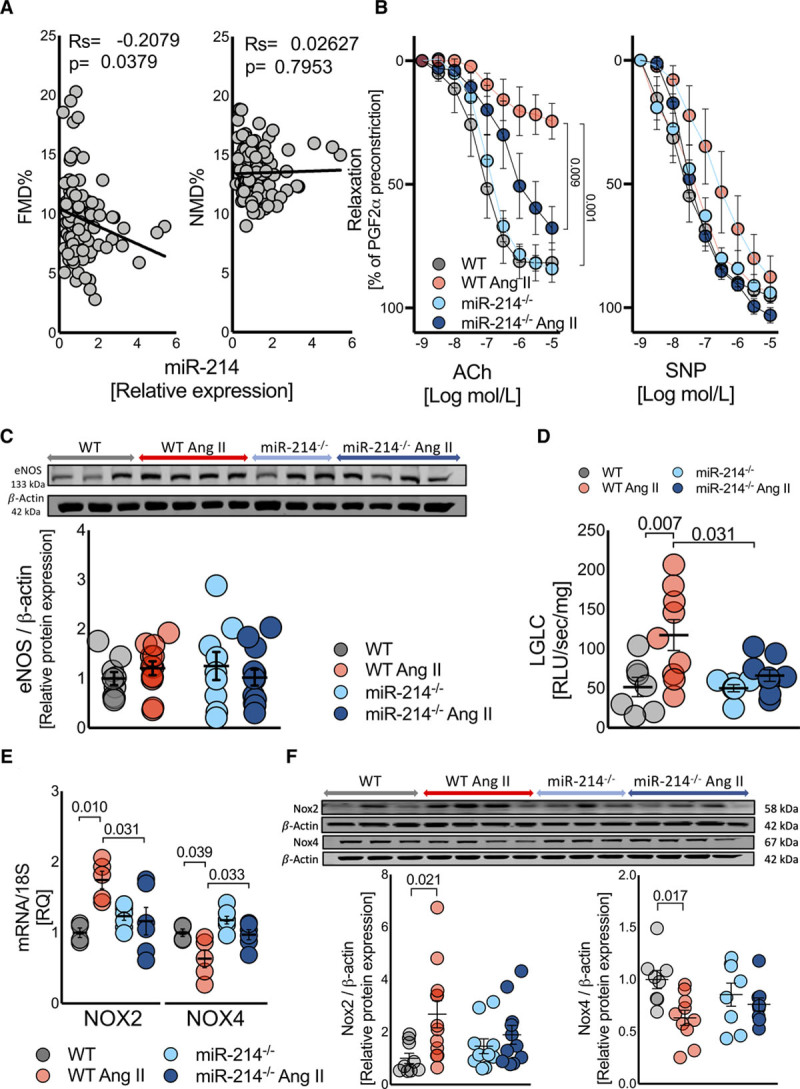
Essential role of miR-214 in endothelial dysfunction and vascular oxidative stress in hypertension. A, Relationship between plasma miR-214 levels and endothelial function (flow mediated dilatation [FMD]) or nonendothelium-dependent relaxations to nitroglycerin (NMD) in humans (n=100). B, Isometric tension studies of endothelium dependent (acetylcholine; ACh) and independent (sodium nitroprusside [SNP]) vasorelaxations (n=5–7/group) using wire myography in sham buffer and Ang II (angiotensin II) infused WT and miR-214−/− mice. C, eNOS (endothelial nitric oxide synthase) protein level in mouse aortas (Western blotting; n=9–12/group). D, Aortic superoxide production measured by lucigenin (5 μM) enhanced chemiluminescence (n=7–9/group). E, Aortic Nox2 and Nox4 mRNA expression (n=5/group) and (F) protein levels in aortas of sham and Ang II infused miR-214−/− and WT mice (n=9–12/group). Data presented as mean±SEM and analyzed by Spearman rank correlation test (A), repeated measures 2-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction (B) or 2-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test (C–F; P values adjusted for 6 comparisons). Overall P values for repeated measures 2-way ANOVA; B for Ach (PResponse=0.0009, PGroup=0.044, PResponse×Group=0.016) and SNP (PResponse=04.1×10−7, PGroup=0.049, PResponse×Group=0.217). Two-way ANOVA; C (PAngII=0.949, PGenotype=0.862, PAngII×Genotype=0.235); D (PAngII×Genotype=0.061, PAngII=0.0042, PGenotype=0.051); E for Nox2 (PAngII×Genotype=0.0062, PAngII=0.193, PGenotype=0.203) and Nox4 (PAngII×Genotype=0.331, PAngII=0.002, PGenotype=0.005); F for Nox2 (PAngII=0.0096, PGenotype=0.683, PAngII×Genotype=0.116) and Nox4 (PAngII=0.0093, PGenotype=0.924, PAngII×Genotype=0.109).
