Figure 2.
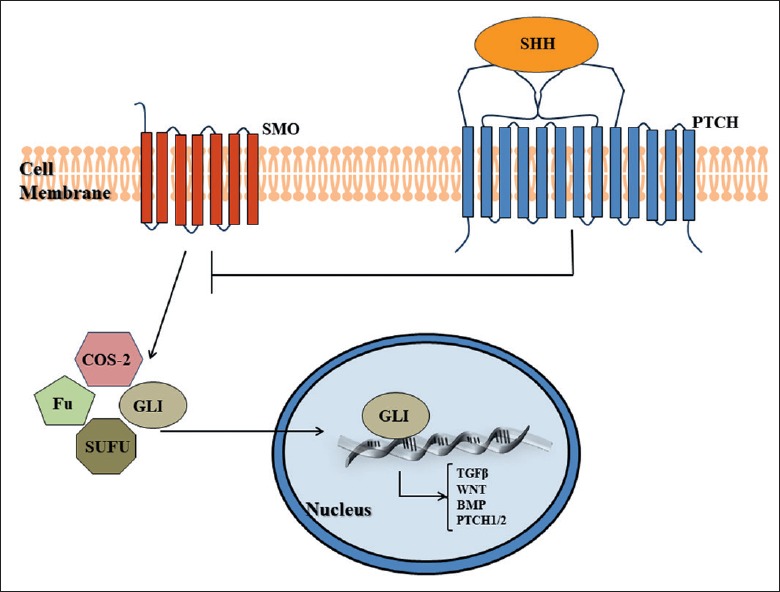
Sonic hedgehog (SHH) pathway. The PTCH1 gene encodes for a receptor protein of the SHH pathway, the Patched1 (PTCH1) receptor. PTCH1 receptor is allocated in the cell plasma membrane and functions as a receptor for ligands of the SHH proteins. PTCH1 receptor constitutively inhibits the next step in SHH pathway. The protein SHH ligand binds to PTCH1 receptor, resulting in a complex in which PTCH1 receptor becomes inhibited releasing the downstream signalling pathway. PTCH1 gene is a tumour suppressor gene as PTCH1 receptor inhibits smoothened (SMO), a seven-transmembrane G-coupled protein receptor expressed by the SMO gene located in chromosome 7q32, which acts as signal transducer of SHH pathway. SMO behaviour is consistent with a proto-oncogene. Activated SMO internalises from plasma membrane and releases GLI proteins from SUFU inhibition which is expressed by SUFU gene located in chromosome 10q24-q25. GLI proteins comprise the transcription factors GLI1, GLI2 and GLI3 which are brought into the cell nucleus. GLI1 protein is a transcriptional activator, while GLI2 and GLI3 proteins may function as activators or as repressors. They have DNA-binding zinc-fingers and activate target genes involved in cell growth and proliferation (PDGFRA, Fox family genes, MYC, cyclins, CTNNB1-, β-catenin- and RUNX3) (from Madan et al., 2010 35, mod.).
