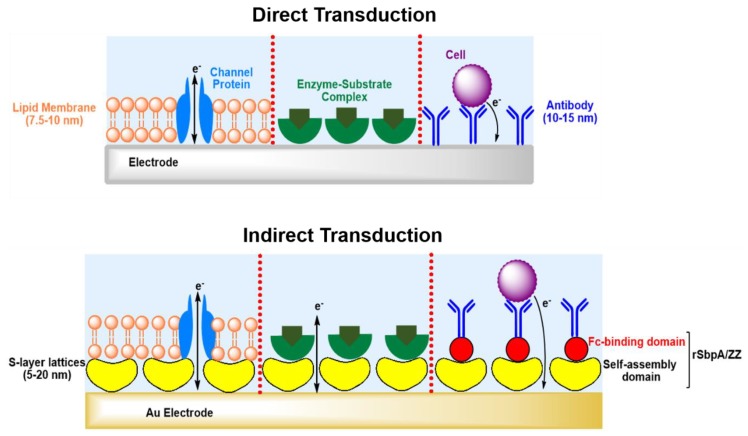
Figure 6.
Direct and indirect transduction (not drawn to scale). In direct approach, the electron transfers are close to the surface, whereas in the indirect one, electron shuttles between the reaction site and the sensor surface. In the proposed model, the S-layer protein lattice constitutes an intermediate matrix. In the lipid-based biosensor (left), electrons transfer from the outer membrane to the inner membrane and vice versa via a channel protein. In the detection biosensor (middle and right), electrons transfer between the enzyme–substrate complex and cell/antibody and electrode surface, respectively. The S-layer lattice provides an immobilization matrix and ion reservoir. The pores of the S-layer lattice ensure no impact on the electron transfer. Fc: fragment crystallizable; rSbpA/ZZ: recombinant S-layer protein from Lysinibacillus sphaericus CCM 2177 with fused Fc-binding Z-domain (synthetic analog of immunoglobulin G (IgG-binding B—domain) of protein A of Staphylococcus aureus).