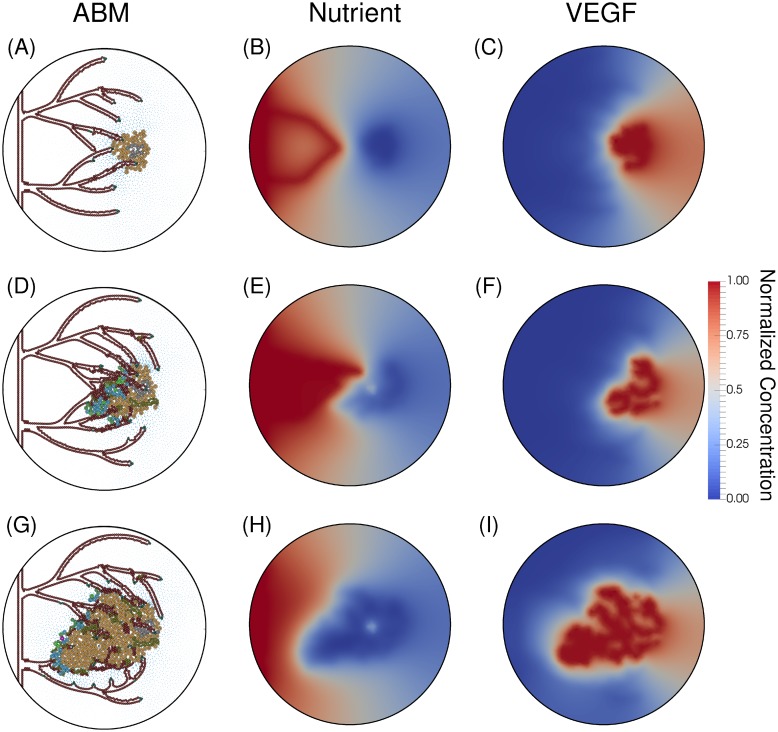
Fig 10. Anastomotic loop formation.
The first anastomotic loop is formed at hour 3100 (Panels A-C). Panel A depicts a newly anastomosed vessel and Panel B the subsequent influx of nutrient delivered by the vessel. The tip cell of the top anastomosed vessel fused into the cells on the wall of the bottom anastomosed vessel (as dictated by the process described in the Model Development Branching subsection). At hour 3800 (Panels D-F), the tumor has become proliferative because of the supplied nutrients from the vessels (Panel E). The complexity of this vascular system is depicted in Panel E, with numerous junctures of vessels and the corresponding nutrients supplied by these vessels. With the decreasing number of hypoxic cells and the increase in vasculature, the concentration of VEGF, shown in Panel F, is quite depleted. Panel G (hour 4000) shows the resulting tumor and vasculature after the tumor has rapidly proliferated due to the influx of nutrients. The stresses imparted on the vasculature by the proliferating tumor cells has severed most of the vessels proximal to the tumor. The resulting nutrient field (Panel H) has no vessels releasing nutrients, as all anastomosed loops have been severed. With the reduction of supplied nutrients, the tumor becomes hypoxic and the production of VEGF increases again (Panel I).