Figure 5:
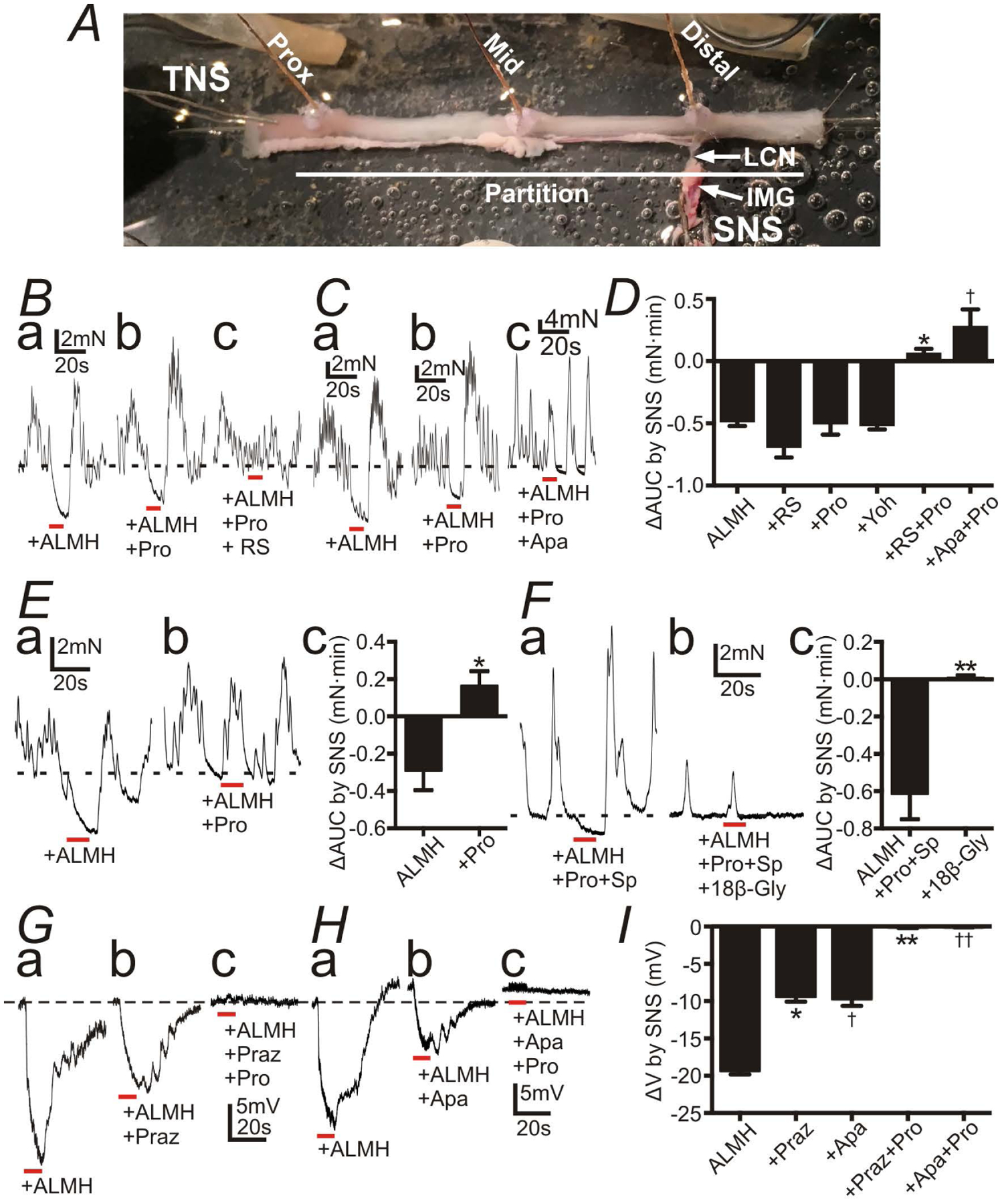
Responses of the distal colon to sympathetic nerve stimulation (SNS) with atropine (1 μM) (A), L-NNA (100 μM) (L), MRS2500 (1 μM) (M), hexamethonium (100 μM) (H) (ALMH) in the bath solution. All red bars represent SNS at 20 Hz at 150 V for 10 s (pulse duration: 0.3 ms). All black dot-lines represent the control baseline of contractions or the resting membrane potentials. A: A preparation for the tension recordings with the lumber colonic nerve (LCN) and the inferior mesenteric ganglion (IMG) intact. B and C: Contractile experiments of WT mouse. SNS caused inhibition of contractions (Ba and Ca). Propranolol (Pro; 10 μM) didn’t block inhibitions by SNS (Bb and Cb), but Pro+ RS100329 (RS; 100 nM) (Bc) or + apamin (Apa; 300nM) (Cb) blocked them (Bc and Cc). D: Summary of ΔAUC (mN•min) by SNS (AUC during SNS - the 10s average of AUC before SNS). * and†P < 0.0005, significant difference from ΔAUC with any single reagent. E: Contractile experiments of Adra1a−/− mouse. SNS relaxed distal colon (Ea) and Pro blocked inhibitions by SNS (Eb). Ec shows summary of ΔAUC (mN•min) by SNS. * P < 0.05. F: Contractile experiments of WT mouse with Pro and substance P (Sp; 1 μM). SNS relaxed distal colon (Fa). 18β-Glycyrrhetinic acid (18β-Gly; 100 μM) blocked inhibitions by SNS (Fb). Fc showed summary of ΔAUC (mN•min) by SNS. ** P < 0.005. G-H: Intracellular electrical recordings of SMCs of WT mouse. SNS induced fast and slow phases of hyperpolarization (Ga and Ha). Prazosin (Praz; 1 μM) or Apa inhibited the fast hyperpolarization (Gb and Hb), and Pro inhibited the residual slow hyperpolarization (Gc and Hc). Resting membrane potential were: G, −48 mV; H, −51mV. G and H were recorded from different tissues. Each record in a given set of three was obtained from the same impalement. I: Summary of ΔV (mV) (induced hyperpolarization by SNS). * and†P < 0.0001, significant difference from ΔV of control. ** and††P < 0.0001, significant difference from Praz and Apa respectively.
