Figure 6:
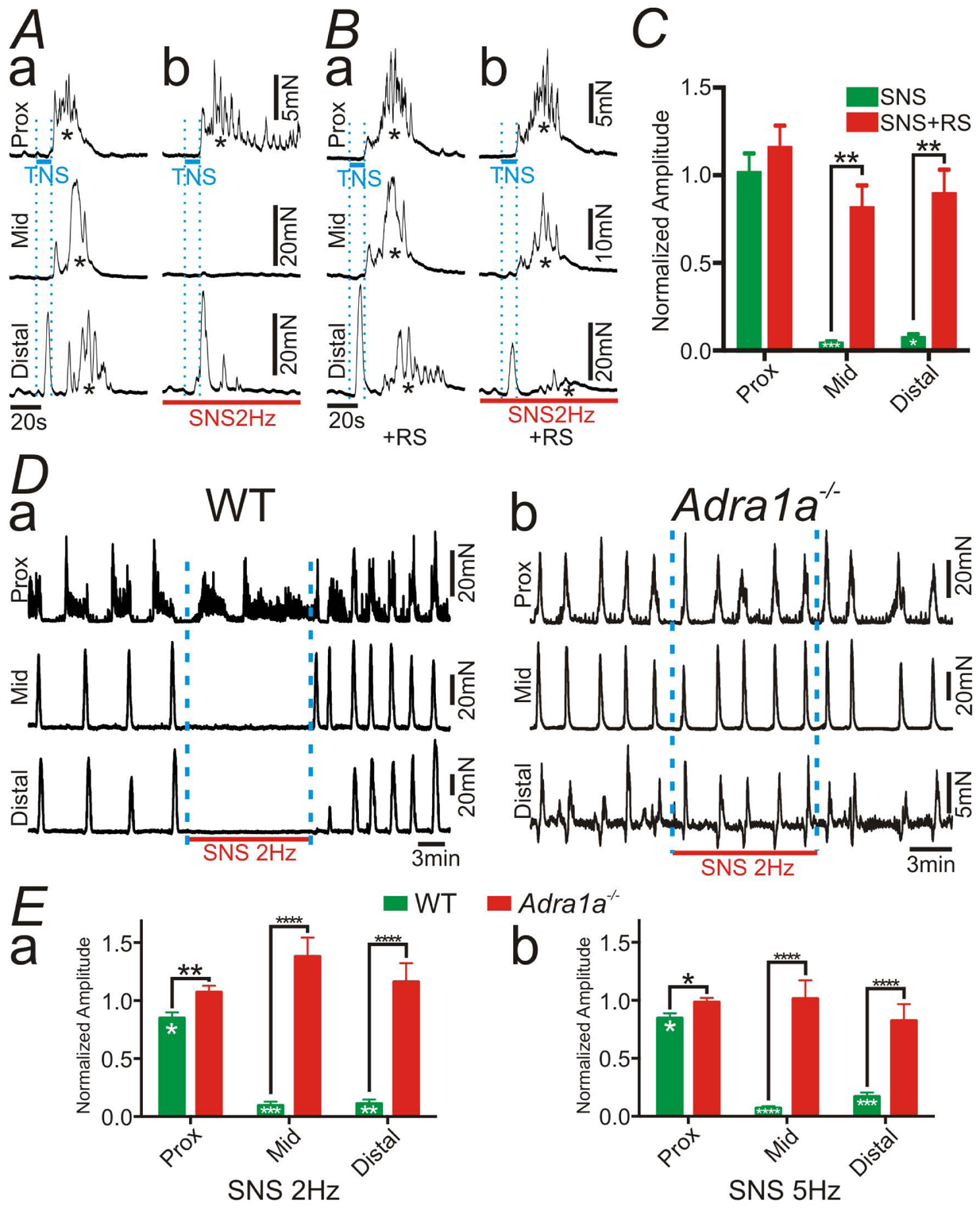
Tension recordings at proximal (Prox), mid and distal colon in the preparation shown in Figure 5A. In this experiment, transmural nerve stimulation (TNS) across wall of proximal colon (blue bars in A and B) elicited the colonic migrating motor complex (CMMC; indicated by *). A: Sympathetic nerve stimulation (SNS; 2 Hz; red bars in A and B) inhibited CMMC at mid and distal colon (Ab). B: The inhibitory effects of SNS (2Hz) on CMMC were blocked by RS100329 (RS; 100nM) (Ba and c). C: Summary of normalized amplitude of CMMC with SNS. RS attenuated the inhibitory effects of SNS. D: Spontaneous CMMC were inhibited by SNS (2 Hz) in WT mouse (Da), however CMMC were not affected by SNS (2 Hz) in the colon of Adra1a−/− mouse (Db). E: Summary of normalized amplitude of CMMC with SNS at 2 Hz (Ea) and 5 Hz (Eb). Deletion of the gene encoding α1A ARs blocked the inhibitory effects of SNS. In panels of C and E, Black asterisks denote statistically significant differences between the values connected by black lines and white asterisks mean statistically significant differences between the amplitude with SNS and the control. The numbers of asterisks mean the same as those in Fig. 2.
