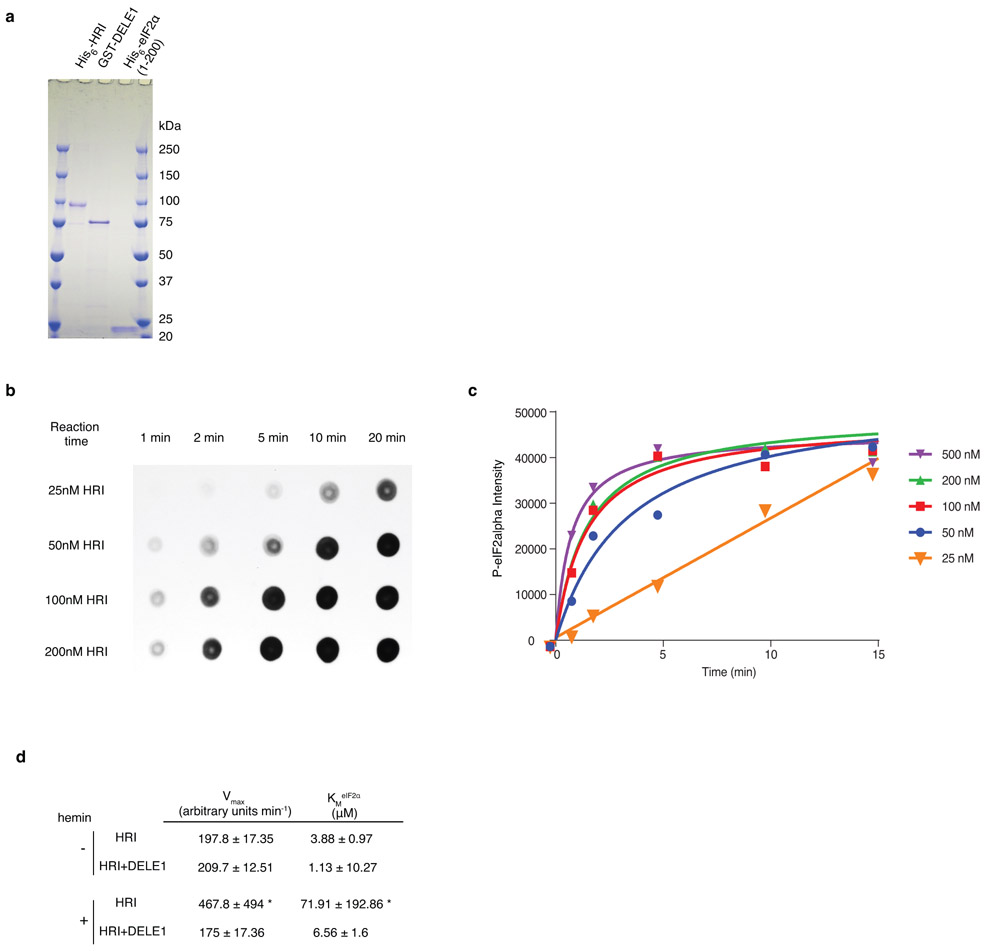
Extended Data Figure 4. The protein kinase assay of purified HRI.
(a) Purified recombinant HRI, DELE1 and eIF2α. 800 ng of each recombinant protein was subjected to SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie blue (n = 1 gel).
(b,c) HRI kinase reactions were performed with 1 μM recombinant yeast eIF2α and various amounts of purified recombinant HRI protein. Reactions were stopped at the time points indicated by removing 5-μl aliquots of the kinase reaction mixture and mixing with equal volume of 2×SDS loading buffer. The SDS samples were then dotted on nitrocellulose blots and subjected to immunoblotting analysis with eIF2αP IgGs. (b) Representative dot blot. (c) Densitometric quantification of dot blots expressed as average value from n = 2 individual experiments. To enable a linear range reaction, 25nM HRI and 5 min incubation time were used for all the subsequence experiments.
(d) Enzyme kinetic constants for HRI activity with or without DELE1 in the presence or absence of hemin (mean ± s.e.m., n = 3 individual reactions, fit for data shown in Fig. 4f). Kinetic constants were determined by fitting to the Michaelis-Menten equation using least-squares fit using Prism version 6.07. * The constants calculated from HRI + hemin are not accurate because under the current substrate concentration range, the enzymatic reaction is first order, never reaching Vmax. But higher substrate concentrations cannot be used to obtain Vmax conditions, as purified eIF2α protein will precipitate at higher concentrations.