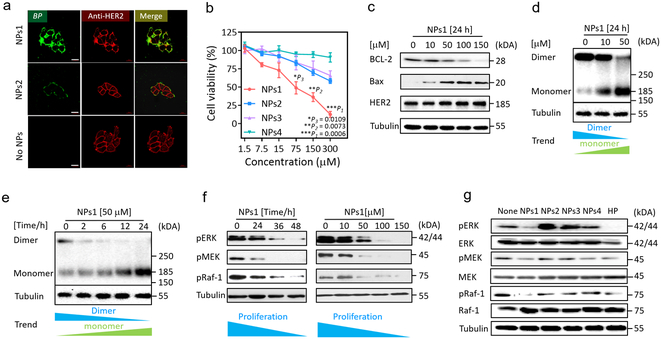
Fig. 3. The extracellular and intracellular mechanisms of fibrillar-transformable nanoparticles interaction with MCF-7/C6 breast cancer cells.
a, Fluorescence binding distribution images of NPs1 and NPs2 binding HER2 receptors of MCF-7/C6 cells for 8 h. HER2 antibody (29D8 rabbit Ab and HER2 peptide of NPs1 and NPs2 recognize different epitopes of HER2 receptor) was used to label HER2 receptors. The concentration of NPs1 and NPs2 were 50 μM. The scale bar in a is 20 μm. Experiments were repeated three times. b, The viability of MCF-7/C6 cells after incubation with NPs1-4 at the different concentration for 48 h. Data are presented as the mean ± s.d., n = 3 independent experiments. The statistical significance was calculated via a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with a Tukey post-hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. c, Western blot analysis of apoptosis related proteins and HER2 total protein in MCF-7/C6 cells treated by NPs1 for 24 h with different concentration. Experiments were repeated three times. d,e, Western blot analysis of inhibition and disaggregation mechanism of HER2 protein dimer in MCF-7/C6 cells treated by NPs1 (d) for 24 h with different concentration and (e) at 50 μM under different time point. Experiments were repeated three times. f, Western blot analysis of inhibition mechanism of proliferation protein in MCF-7/C6 cells treated by NPs1 at 50 μM under different time point and at 24 h under different concentration. Experiments were repeated three times. g, Western blot analysis of inhibition mechanism of proliferation protein in MCF-7/C6 cells treated by NPs1-4 and Herceptin (HP) at 36 h. The concentration of NPs1-4 were 50 μM, and the concentration of Herceptin was 15 μg/mL as a positive control group. Experiments were repeated three times.