Fig. 1 |. Causes and consequences of low-grade systemic chronic inflammation.
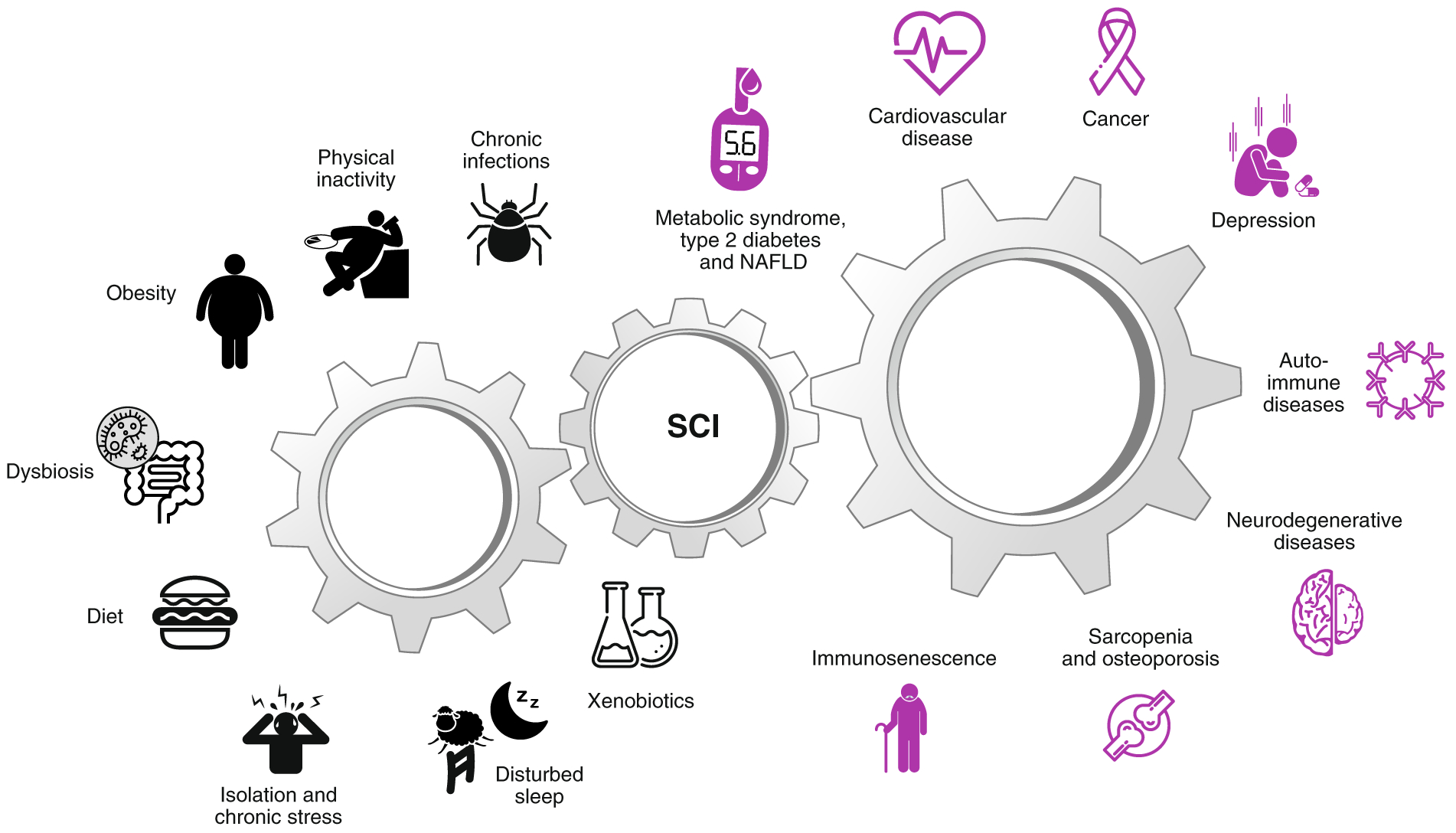
Several causes of low-grade systemic chronic inflammation (SCI) and their consequences have been identified. As shown on the left, the most common triggers of SCI (in counter-clockwise direction) include chronic infections, physical inactivity, (visceral) obesity, intestinal dysbiosis, diet, social isolation, psychological stress, disturbed sleep and disrupted circadian rhythm, and exposure to xenobiotics such as air pollutants, hazardous waste products, industrial chemicals and tobacco smoking. As shown on the right, the consequences of SCI (in clockwise direction) include metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), cardiovascular disease, cancer, depression, autoimmune diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, sarcopenia, osteoporosis and immunosenescence.
