Fig. 3. Silicone substrates have high surface energies and surface stresses.
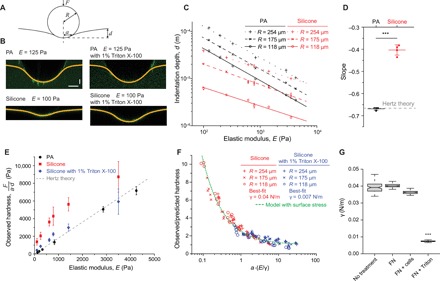
(A) Schematic depicting the indentation of a rigid indenter (steel ball) into an elastic substrate. (B) Confocal fluorescence images showing the surface profiles of PA gels (E = 125 Pa; top left) and silicone gels (E = 100 Pa; bottom left) submerged in buffer or buffer with 1% Triton X-100 and indented by steel balls with radii of 254 μm. Horizontal scale bar, 100 μm; vertical scale bar, 30 μm. (C) Indentation depth, d, of the steel ball versus substrate elastic modulus, E, for PA and silicone gels of the indicated stiffness. Steel balls used were 254, 175, or 118 μm in radii, as indicated; n ≥ 5. (D) Slopes of the log-log scale plots shown in (C). Hertz contact theory predicts a slope of −2/3. ***P < 0.001, t test; n = 4. Error bars show SEMs. (E) Observed substrate hardness, F/(a∙d), versus elastic modulus; F is the indentation force, and a is the measured contact radius of the indenter. The dashed line shows the prediction by Hertz contact theory; n ≥ 12. Error bars show SEMs. (F) Ratio of observed and predicted hardness, (a*∙d*)/(a∙d), versus the elastocapillary number, a∙(E/γ), for silicone gels submerged in buffer or buffer with surfactant. a* and d* are the Hertz predicted contact radius and indentation depth, respectively. Experimental data converge on a theoretical model of contact for an elastic substrate having surface tension. Best-fit surface tensions are 0.04 and 0.007 N/m for measurements in buffer and buffer with surfactant, respectively. (G) Best-fit surface tensions of silicone substrates with no adsorbed surface proteins (No treatment), adsorbed with fibronectin (FN), adsorbed with fibronectin and measured after 24 hours of culture with MEC cells (FN + cells), or adsorbed with fibronectin and treated with 1% Triton X-100 (FN + Triton). ***P < 0.001, t test; n ≥ 100. Horizontal lines are medians. Boxes show the IQR. Whiskers extend to minimum and maximum values.
