Figure 2. Sex- and spatial- heterogeneity of microglia early in development.
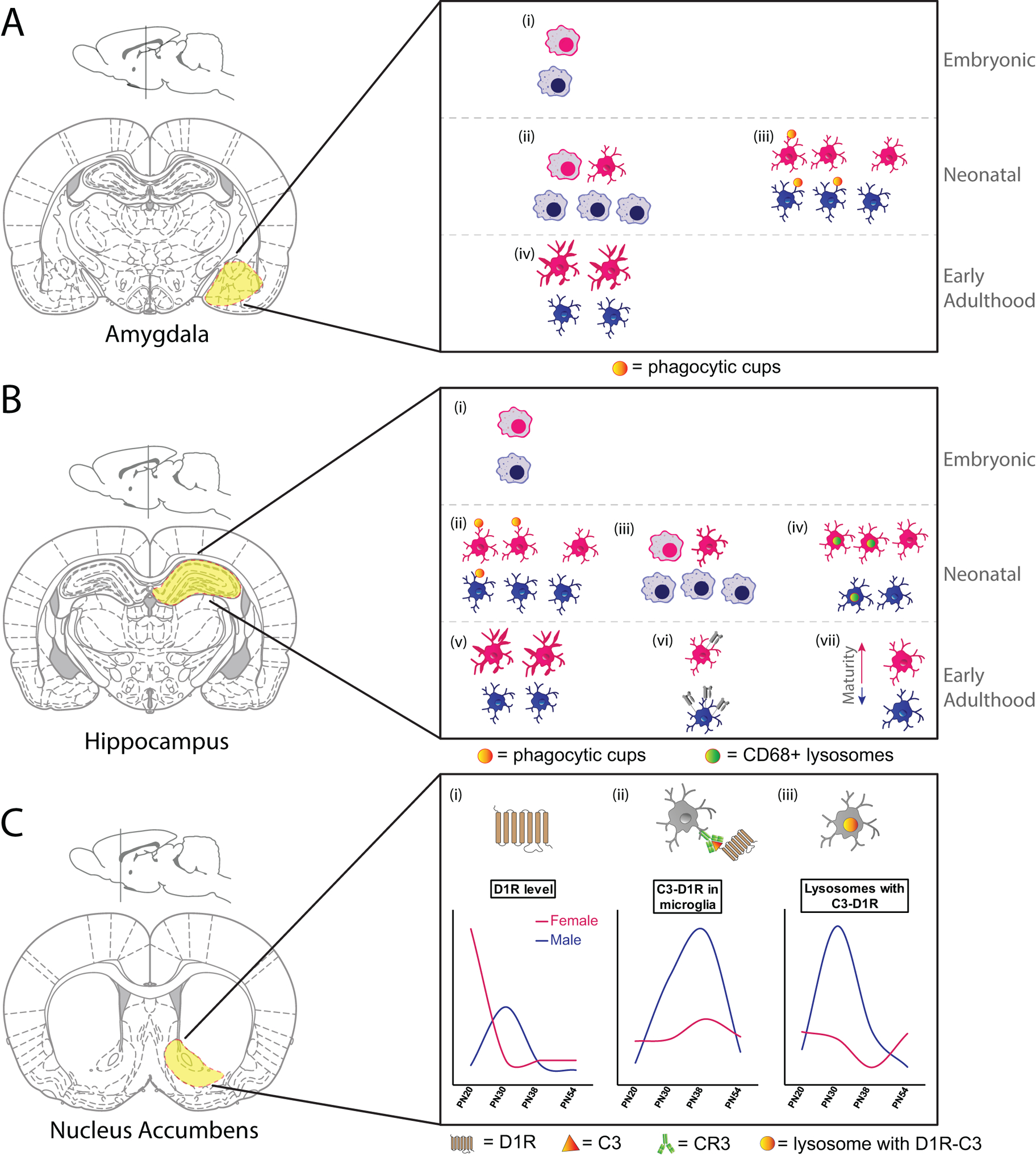
A. (i) There are no sex differences in microglial number or morphology in the E17 amygdala, with the majority of both male and female microglia showing amoeboid morphology. (ii) By PN4 male amygdala had more microglia and a higher proportion of microglia with amoeboid morphology than females. (iii) On PN2 and PN4, male microglia within the amygdala had more microglia with phagocytic cups than did females. (iv) By PN30, microglial morphology within the amygdala had shifted towards a more ramified/complex state. At this time females had more microglia with long, thick processes than males.
This figure is based on data presented in (Schwarz, Sholar, and Bilbo 2012; VanRyzin et al. 2019)
B. (i) There are no sex differences in microglial number or morphology in CA1 or CA3 regions of the hippocampus at E17, with the majority of both male and female microglia showing amoeboid morphology. (ii) At PN3, female rat hippocampus had more microglia with phagocytic cups than male hippocampus. (iii) By PN4 male hippocampus had more microglia and a higher proportion of microglia with amoeboid morphology than females. (iv) Females in PN8 hippocampus had more microglia and more CD68 intensity within microglia than males. (v) By PN30, microglial morphology within the hippocampus had shifted towards a more ramified/complex state. At this time females had more microglia with long, thick processes than males. (vi) 3-week old male mice had more MHC I expression on microglia (CD11b+CD45high cells) isolated from hippocampus than females. (vii) Microglial maturation (determined by microglial developmental index) was lower in microglia isolated from the hippocampus of a PN60 male mouse than from a female mouse.
This figure is based on data presented in (Schwarz, Sholar, and Bilbo 2012; Hanamsagar et al. 2017; Nelson, Warden, and Lenz 2017; Weinhard et al. 2018; Guneykaya et al. 2018)
C. (i) Dopamine D1 receptor levels in the nucleus accumbens peak at PN20 in females and are downregulated by PN30, whereas D1R levels peak at PN30 in males, and are then downregulated. (ii) Co-localization of microglial C3 and D1R peak in males at PN30 and PN38, with only a small upregulation seen by PN38 in females. (iii) CD68+ microglial lysosomes containing co-localized C3 and D1R peak in males at PN30, with a minor dip seen in females at PN38.
This figure is based on data presented in (Kopec et al. 2018).
