FIG 2.
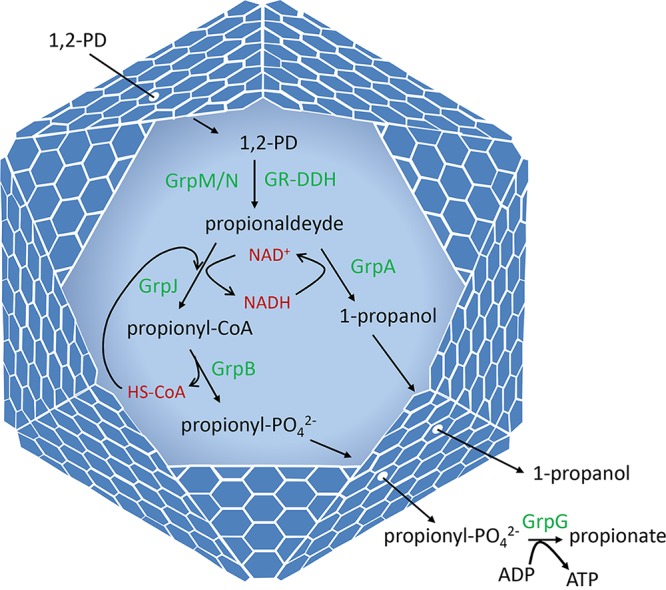
Model for 1,2-PD degradation by the Grp MCP of E. coli CFT073. The Grp MCP allows E. coli CFT073 to grow by 1,2-PD fermentation. 1,2-PD diffuses through the protein shell of the MCP and enters the lumen, where it is converted to propionaldehyde by a glycyl radical diol dehydratase (GrpM) supported by its activating enzyme (GrpN). Propionaldehyde is further metabolized to 1-propanol and propionate by the GrpJ aldehyde dehydrogenase, the GrpA alcohol dehydrogenase, the GrpB phosphotransacylase, and the GrpG propionate kinase. This pathway generates ATP, which is used to support growth. Based on analogy with other MCPs, its likely function is to sequester propionaldehyde to prevent toxicity and/or diffusive loss through the cell envelope. Also based on analogy, the GrpJ aldehyde dehydrogenase and the grpA 1-propanol dehydrogenase are likely required for recycling coenzyme A (HSCoA) and NAD+, respectively, internally within the MCP.
